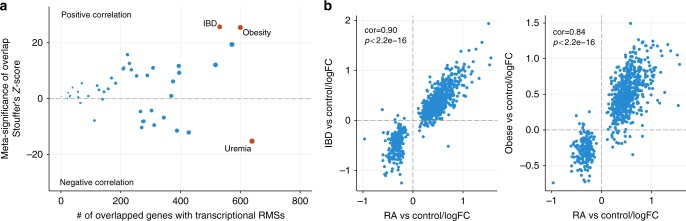
Fig. 6.
The presence of the RA-associated RMS in other disease conditions. a The disease-wide landscape of RA RMS. The comparisons of the RA untreatable transcript signature and publicly available disease signatures from whole blood or PBMCs were assessed by Fisher’s exact test in the NextBio database. The p values from multiple studies of the same diseases were combined by Stouffer’s z-score method. The size of the dots is proportional to the number of overlapped genes with the RA-associated untreatable transcript signatures. The red dot represents diseases with z-scores that were higher than the top 5% of z-scores over all diseases examined. b The changes in expression were similar for the transcriptional RMS between RA and the most associated diseases. The fold changes in the 800 transcriptional RMS between patients and controls were calculated using the raw data from the IBD study (GSE33943; n = 45 for IBD and n = 15 for controls) and the obesity study (GSE18897; n = 29 for obese and n = 20 for controls). The fold changes from each study were then compared with those determined for our RA cohort (n = 45 for RA and n = 35 for HCs)