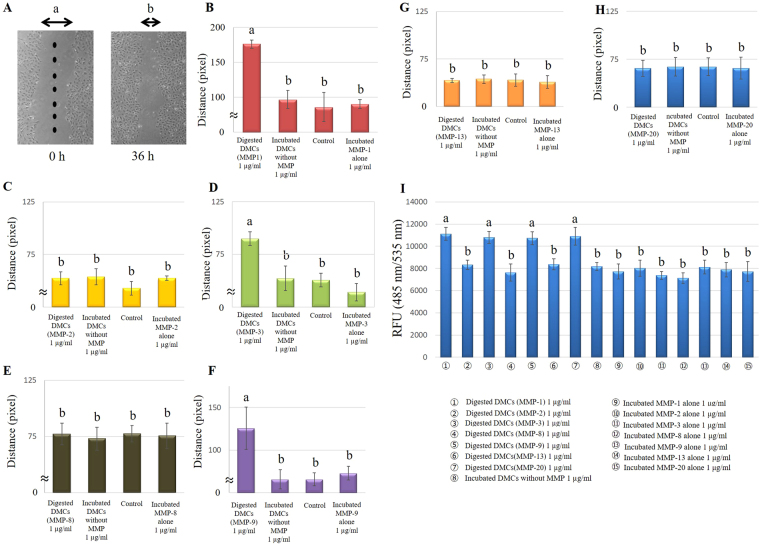
Figure 3.
Effects of 1 µg/ml of dentin matrix components (DMCs) treated with matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) on wound scratch (B–H) and chemotactic (I) cell migration. Eight points were randomly selected to assess wound scratch migration; the distances of the cells from the edge of the scratch wound were measured by microscopic observation (A). Wound scratch migration of cells incubated with 1 µg/ml DMCs treated with MMP-1 (B), MMP-2 (C), MMP-3 (D), MMP-8 (E), MMP-9 (F), MMP-13 (G) and MMP-20 (H) is presented as the amount of movement, and chemotactic migration of cells incubated with 1 µg/ml DMCs treated with MMP-1, MMP-2, -3, -8, -9, -13, and -20 is presented as relative fluorescence units (RFU) (I). One microgram per millilitre of DMCs treated with MMP-1, -3, or -9 promoted horizontal migration, compared with 1 µg/ml of incubated DMCs without the addition of MMPs (p < 0.05). The trans-well assay demonstrated the significant chemotactic effects of 1 µg/ml of DMCs treated with MMP-1, -3, -9, or -20, compared with the experimental and negative controls (p < 0.05). Significant differences were not observed with 1 µg/ml DMCs treated with other MMPs, MMPs incubated alone or at lower concentrations (0.01–0.1 µg/ml) of the above-mentioned MMPs. Groups with similar lower-case letters (i.e., a and b) are not significantly different. Data represent five independent experiments.