Figure-1.
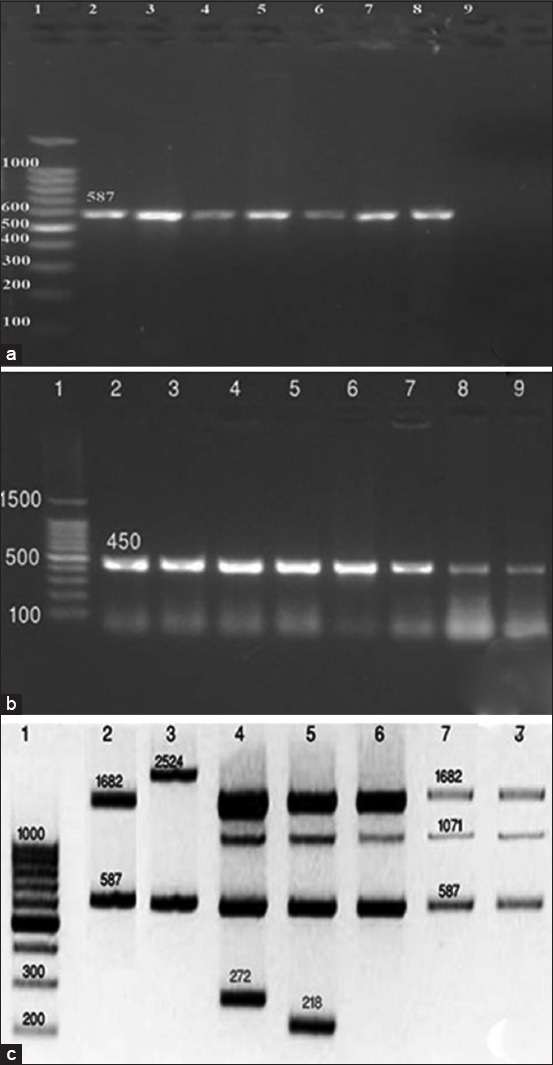
(a) Universal polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primer sequences targeting Erythritol catabolism, gene eryC (Lane 1:100 bp DNA ladder, Lane 2, 3, 4, 5: Brucella cultures (587 bp), Lane 6: Brucella lymph node DNA extract (587 bp), Lanes 7, 8: Brucella melitensis positive control (587 bp), Lane 9: Brucella abortus S19 control). (b): Universal PCR using primer sequences targeting immunodominant antigen, gene bp26 (Lane 1: 100 bp DNA ladder, Lane 2, 3, 4, 5, 6: Brucella cultures (450 bp), Lane 7: B. melitensis3 culture positive control (450 bp), Lane 8, 9: Brucella lymph node DNA extract, 450 bp). (c): Multiplex Bruce-ladder PCR of Brucella isolates (Lane 1: DNA ladder, Lane 2: B. abotus Bruce-ladder kit control (587 bp and 1682 bp), Lane 3: B. abortus RB51 Bruce-ladder kit control (587 bp and 2524 bp), Lane 4: Brucella suis Bruce-ladder kit control (272 bp, 587 bp, 1071 bp, and 1682 bp), Lane 5: B. melitensis Rev1 Bruce-ladder kit control (218 bp, 587 bp, 1071 bp, and 1682 bp), Lane 6: B. melitensis positive control (587 bp, 1071 bp, and 1682 bp), Lanes 7, 8: B. melitensis cultures (587 bp, 1071 bp, and 1682 bp).
