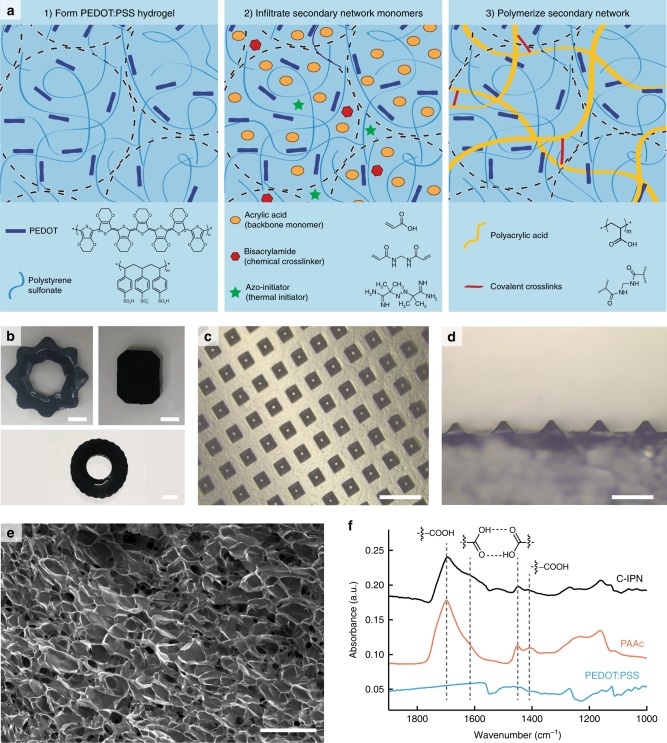
Fig. 1.
Fabrication and structure of C-IPN hydrogels. a Process for fabricating C-IPN hydrogels. First, PEDOT:PSS hydrogels are formed from aqueous solutions of PEDOT:PSS by using ionic liquid to screen the electrostatic repulsions between PEDOT:PSS microgels, enabling them to aggregate into a macroscopically connected network. Second, the PEDOT:PSS hydrogel is infiltrated with acrylic acid, bisacrylamide, and an azo-initiator. Finally, the polyacrylic acid network is formed by polymerizing the monomers in water at 70 °C. b Various large shapes made by casting the PEDOT:PSS/acrylic acid mixture into different silicone soap molds. Scale bars are 1 cm. c, d C-IPN can be micropatterned into pyramidal structures with features as small as 10 μm by casting into silicon molds. Scale bar is 200 μm c and 100 μm d. e Cross-sectional SEM image of freeze-dried C-IPN showing that the final gel is homogeneous and porous. Scale bar is 100 μm. f FTIR spectra of PEDOT:PSS, PAAc, and C-IPN, showing a clear presence of PAAc within the C-IPN composite