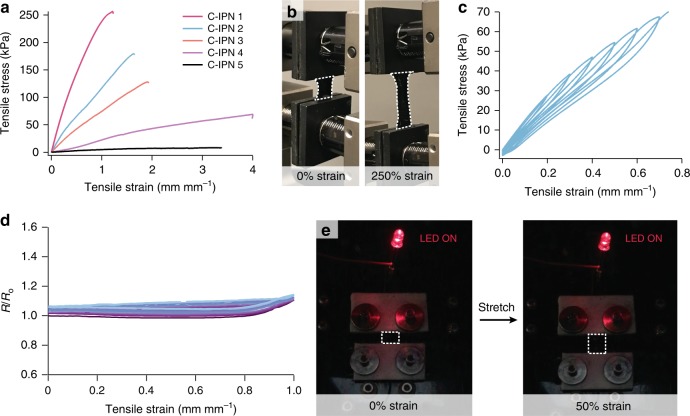
Fig. 3.
Mechanical and strain-dependent properties of C-IPN hydrogels. a Tensile elongation curves of different C-IPN formulations, showing that all formulations can be stretched to over 100% despite large differences in the elastic moduli, which is given by the initial slope of the stress/strain curve. b Picture of a C-IPN 4 gel being stretched to 250%. c Cyclic stress/strain tensile data for C-IPN 2 exhibiting minimal hysteresis, reflecting its excellent elastic properties. d Change in resistance, expressed as a ratio between resistance (R) and initial resistance (Ro), across a C-IPN 2 gel as it is cycled reversibly between 0 and 100% strain for 10 cycles. Despite the large changes in tensile strain, the resistance stays fairly constant near its initial value. e Due to the largely strain independent conductivity of the gels, it is able to keep an LED lit even after being stretched to 50% strain