Fig. 4.
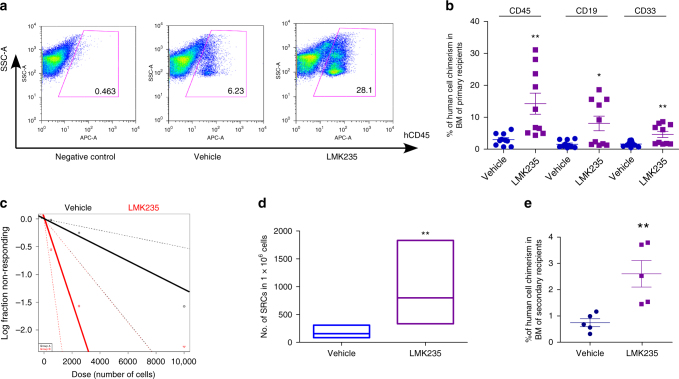
Inhibition of HDAC5 increases long-term engraftment of human CB HSC. a Representative flow cytometric analysis of human engraftment in the BM of NSG mice, 16 weeks after transplantation. Left is from a mouse without transplantation (negative control), center and right are from mice transplanted with human CB CD34+ cells treated with vehicle control or LMK235 for 16 h. Human engraftment was assessed as the percentage of human CD45+ cells. b The percentage of human CD45+ cells, B-cell (CD19+), and myeloid cell (CD33+) chimerism in the BM of NSG mice after transplantation with 10,000 CB CD34+ cells that had been treated with vehicle or LMK235. The data were pooled from two independent experiments (n = 10 mice per group, t-test, *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01). c,d The frequency of human SRCs in CB CD34+ cells treated with vehicle control or LMK235. c Poisson statistical analysis of data from Supplementary Table 3. n = 30 mice in total. Shapes represent the percentage of negative mice for each dose of cells. Solid lines indicate the best-fit linear model for each data set. Dotted lines represent 95% confidence intervals. d HSC frequencies (line in the box) and 95% confidence intervals (box) presented as the number of SRCs in 1 × 106 CD34+ cells. **p < 0.01. e Human CD45+ cell chimerism in the BM of secondary recipient NSG mice at 16 weeks, which had been transplanted with 5 × 106 BM cells from primary recipient NSG mice (n = 5 mice per group, t-test, **p < 0.01). For all panels, data are shown as dot plots (mean ± SEM)