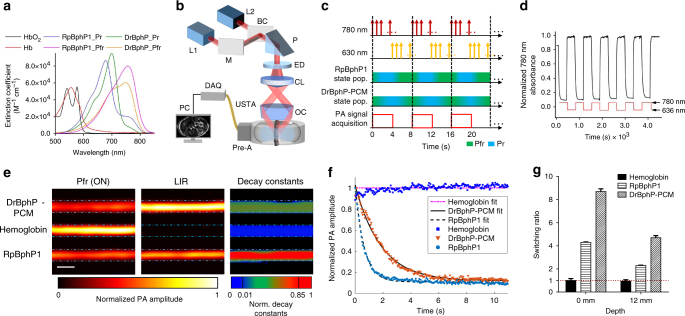
Fig. 1.
Spectral and photoacoustic characterization of the DrBphP-PCM. a Molar extinction spectra of oxy-hemoglobin (HbO2), deoxy-hemoglobin (Hb), Pfr (ON), and Pr (OFF) state of DrBphP-PCM and RpBphP1. b Schematic of the whole-body photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) system with a ring-shaped illumination pattern. BC beam combiner, CL conical lens, DAQ data acquisition unit, ED engineering diffuser, M mirror, OC optical condenser, P prism, PC personal computer, pre-A pre-amplifier, USTA ultrasonic transducer array. L1, a Ti:Sapphire laser fired at 780 nm is used for PA imaging and switching off BphPs. L2, the optical parametric oscillator (OPO) laser, fired at 630 nm, switches BphPs ON. c Time sequence of photoswitching and imaging of BphPs (pop., population). d Absorbance of DrBphP-PCM at 780 nm, switched OFF with 780 nm light illumination and then switched ON with 630 nm illumination. The photoswitching period was 180 s for both wavelengths. e PA images of transparent silicone tubes filled with proteins in clear media. Left column: ON state PA image of BphPs and hemoglobin, middle column: frequency lock-in reconstructed (LIR) PA image of BphPs and hemoglobin; right column, decay constant encoded image showing a reliable separation of DrBphP-PCM, RpBphP1, and non-switchable hemoglobin. Scale bar, 500 µm. f PA signal changes upon 780 nm light illumination and their fits, where PA signals from either DrBphP-PCM or RpBphP1 exponentially decrease during photoswitching, but with different decay constants. However, the blood signal remains at the original level. Thus, the difference in decay constants enables a good separation of hemoglobin, DrBphP-PCM, and RpBphP1. g The switching ratio of BphPs and hemoglobin, defined as the ratio between the ON and OFF states of the PA amplitude, in both clear medium (0 mm in depth) and scattering medium (12 mm in depth); error bars are s.e.m. (n = 40), calculated based on the pixel values from regions of interest