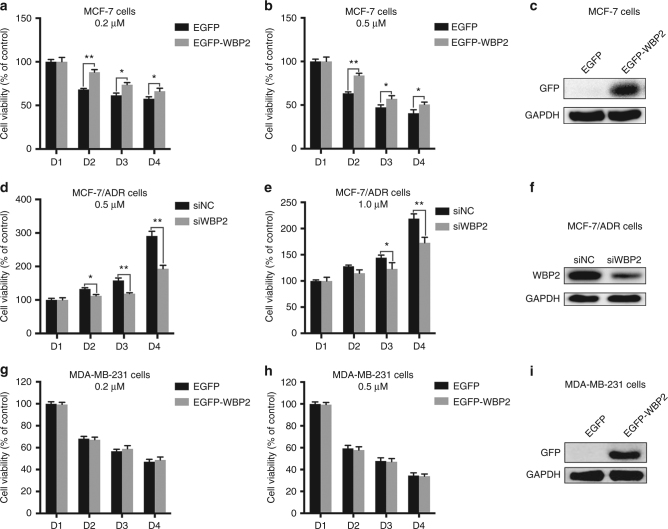
Fig. 2.
Effects of WBP2 on cell viability in doxorubicin-treated MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR cell viability. Measurement of cell viability using MTT assay in control MCF-7 cells and WBP2-overexpressing MCF-7 cells treated with 0.2 μM (a) and 0.5 μM (b) doxorubicin for 0, 24, 48 and 72 h. c WBP2 overexpression efficiency was verified by performing western blotting in MCF-7 cells. Measurement of cell viability using MTT assay in MCF-7/ADR cells and RNAi-mediated WBP2 knockdown in MCF-7/ADR cells treated with 0.5 μM (d) and 1.0 μM (e) doxorubicin for 0, 24, 48 and 72 h. f Validation of WBP2 knockdown efficiency in MCF-7/ADR cells. Test of cell viability through MTT assay in control MDA-MB-231 cells and WBP2-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 0.2 μM (g) and 0.5 μM (h) doxorubicin for 0, 24, 48 and 72 h. i Validation of WBP2 overexpression efficiency in MDA-MB-231 cells. EGFP, control MCF-7 cells; EGFP-WBP2, WBP2-overexpressing MCF-7 cells; siNC, control MCF-7/ADR cells; siWBP2, RNAi-mediated WBP2 knockdown in MCF-7/ADR cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01