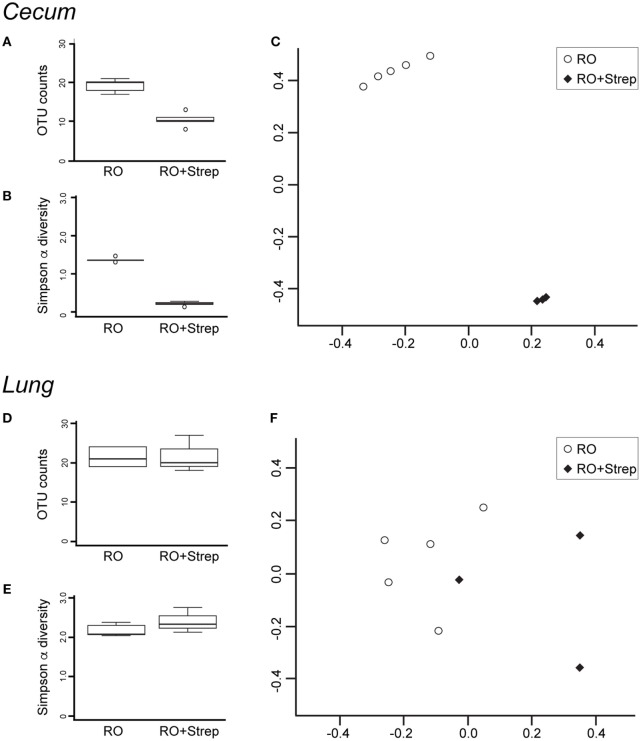
Figure 2.
Streptomycin treatment reduces the abundance and diversity of cecal but not lung microbiota. DNA was isolated from cecum (A–C) and lung (D–F) after 2 weeks of reverse osmosis (RO) or RO + streptomycin treatment, and analyzed for microbial composition. Operational taxonomic unit (OTU) counts (A,D) and alpha diversity (B,E) were compared between treatment groups. Beta diversity was compared using Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling Ordination of the Bray–Curtis beta diversity metric (C,F). (A) Significant differences were seen in cecal OTU count (p = 4.5 × 10−5, n = 5), (B) Simpson alpha diversity index (p = 1.5 × 10−9, n = 5), and (C) beta diversity (Adonis p = 0.012, n = 5, note that two treated samples were so close to the others that the treated group appears as only three samples). No significant differences were noted in lung microbiota (D) OTU composition, (E) Simpson alpha diversity index, or (F) beta diversity between antibiotic-treated (n = 3) and -untreated (n = 5) mice.