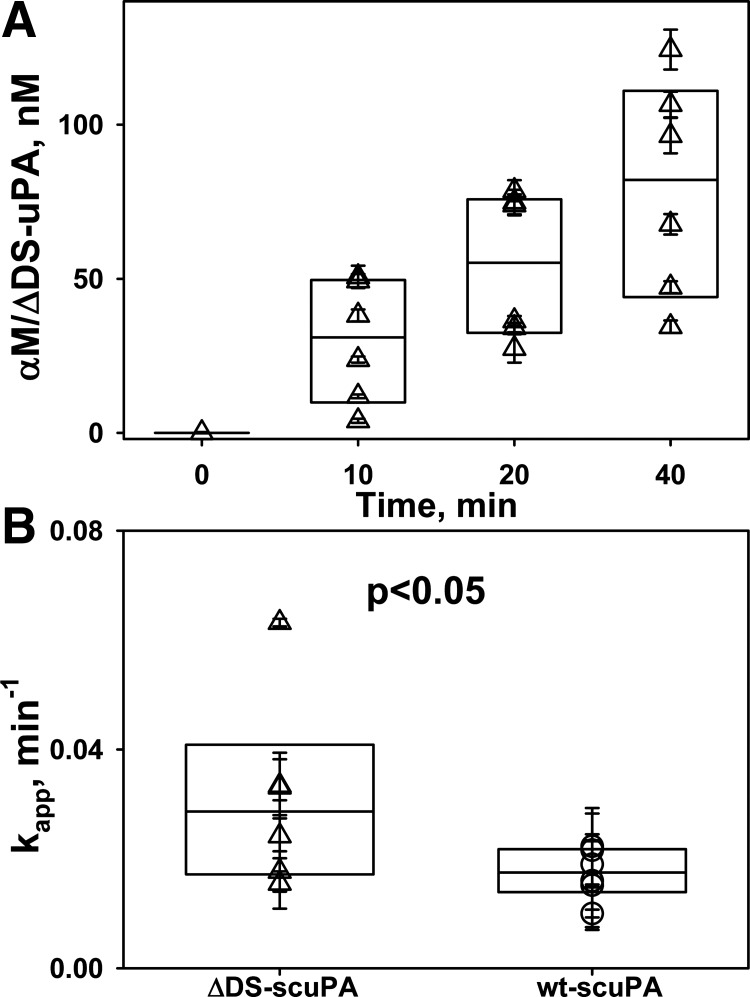
Fig. 5.
Accumulation of intrapleural α-macroglobulin (αM)/urokinase with 179RHRGGS184→179AAAAAA184 substitutions (ΔDS-uPA) “molecular cage” complexes during intrapleural fibrinolytic therapy (IPFT). A: time dependence of the formation of intrapleural αM/ΔDS-uPA during IPFT with ΔDS-scuPA (0.0625 mg/kg). ΔDS-uPA amidolytic activity was measured after samples of pleural fluid withdrawn at 0–40 min were supplemented with an excess (100–200 nM) of exogenous recombinant human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) to inhibit free enzyme. PAI-1-resistant ΔDS-uPA amidolytic activity, which represents intrapleural ΔDS-uPA in “molecular cage” complexes with αM (46, 50), was converted to concentrations (nM) and plotted against time. A single exponential equation was fit to the dependence of the concentration of αM/ΔDS-uPA (A) or αM/uPA (not shown) on time to obtain the values of the apparent first-order rate constants (kapp; B) as previously described (46).