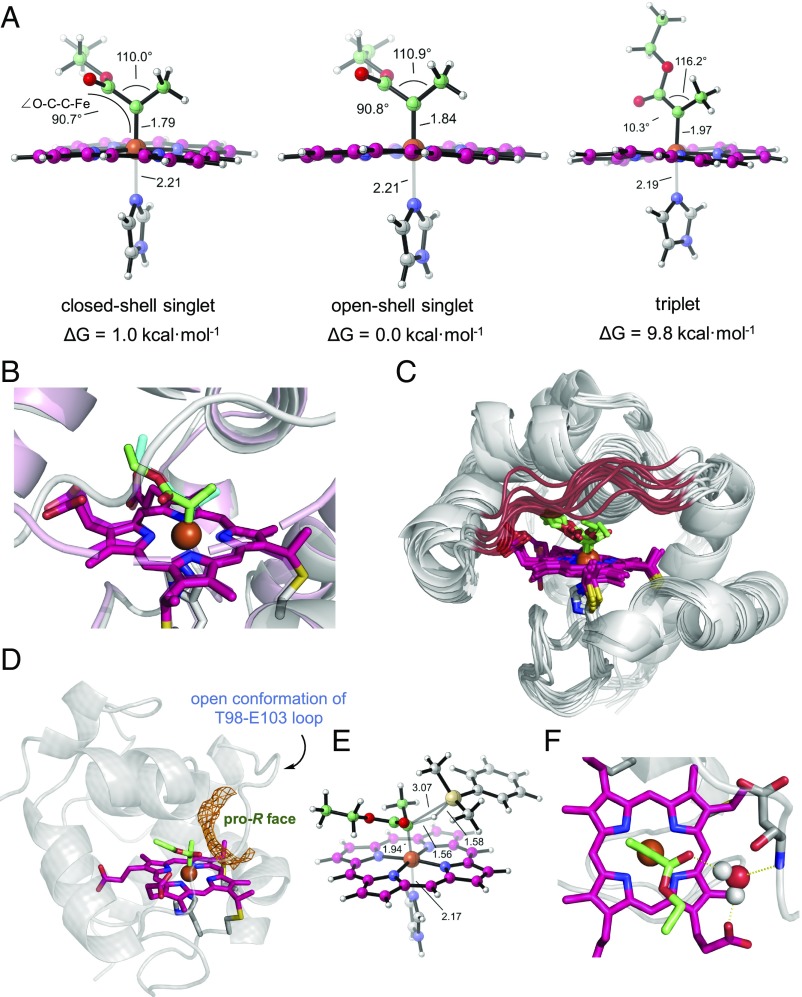
Fig. 3.
Computational models of carbene-bound Rma TDE. (A) DFT optimized structures of model IPC 1 in the closed shell singlet, open shell singlet, and triplet electronic states. DFT calculations predict that the singlet state is 8.8 kcal·mol−1 more stable than the triplet state, which is consistent with previously characterized small molecule IPCs. The calculated Fe–C bond lengths are 1.79, 1.84, and 1.97 Å for the closed shell singlet, open shell singlet, and triplet, respectively. The Fe–N (imidazole) bond lengths are 2.21, 2.21, and 2.19 Å, respectively. These numbers are within experimental error of the lengths observed in the carbene-bound Rma TDE crystal structure, where the Fe–C bond length is 1.9 Å and the Fe–N bond length is 2.1 Å. (B) Overlay of the carbene-bound Rma TDE crystal structure with a QM/MM-optimized structure of carbene-bound Rma TDE. QM/MM structure: protein scaffold is gray, and carbene is green. Crystal structure (PDB ID code 6CUN): protein scaffold is light pink, and carbene is cyan. The preferred carbene conformation determined by MD simulations and QM/MM calculations is almost identical to that determined by X-ray crystallography. (C) Overlay of 10 representative snapshots obtained from 1,000 ns of MD simulation on the carbene-bound Rma TDE. Simulations show that the active site front loop (residues 98–103; highlighted in red) is highly flexible, switching between “open” and “closed” conformations. Despite the front loop’s high flexibility, the carbene is stabilized in a single major conformation (SI Appendix, Fig. S7). (D) Snapshot obtained from an MD trajectory on carbene-bound Rma TDE with the front loop in the open conformation, showing that the carbene pro-R face is solvent exposed. Solvent-accessible area is showed in orange. (E) DFT-optimized structure of the lowest-energy pro-R transition state (closed shell singlet state) for Si–H insertion with IPC 1 (SI Appendix, Fig. S8). (F) A representative view of an MD snapshot on carbene-bound Rma TDE showing interactions between the bridging water with the heme carboxylate, the carbene carbonyl, and the amide bond of residue D100. Hydrogen-bonding interactions with the carbene have been shown to affect the stability of IPCs (25, 27, 37).