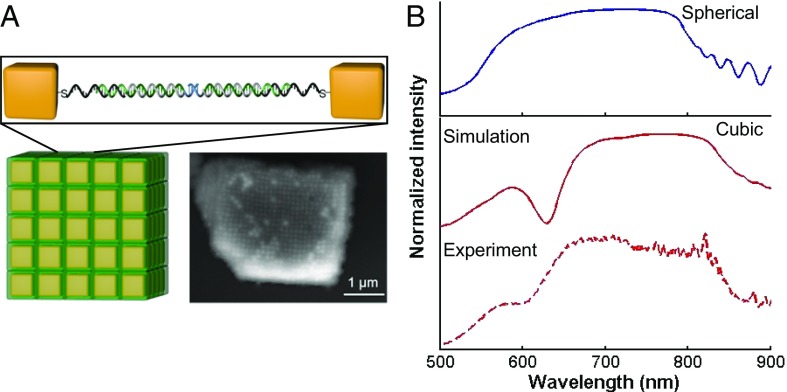
Fig. 5.
Experimental measurement and FDTD simulations of cubic NP superlattices. (A) Schematic representation (Lower Left) and scanning electron microscope image (Lower Right) of a superlattice made through DNA-programmable assembly of nanocubes after encasing in silica. The Au nanocube building blocks have an 88-nm edge length and a 5-nm corner rounding. The lattice constant of the superlattice is 134 nm and defined by the duplex DNA interconnects [sequences used: anchor strand: TCA ACT ATT CCT ACC TAC AAA AAA AAA A SH; linker strand: GTA GGT AGG AAT AGT TGA A TTTTTTTTTTTT ACT GAG CAG CAC TGA TTTTTTTTTTTTT A GCGC; and duplexer strand: AAAAAAAAAAAAA TCA GTG CTG CTC AGT AAAAAAAAAAAA; all strands are listed from 5′ to 3′ (SI Appendix, section 1.3 has details)]. An enlarged view of one hybridized DNA pair between nearest neighbor nanocubes in a lattice is shown in Upper. (B, Upper) Simulation result of a cP superlattice with spherical NPs that has the same lattice constant and volume fraction as the superlattice shown in A. (B, Lower) Simulation and experimental results for the superlattice shown in A.