Fig. 1.
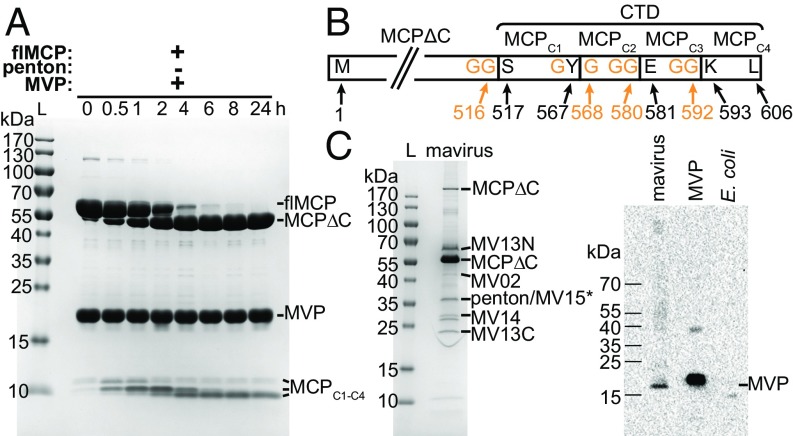
Mavirus MCP is processed by MVP in vitro and in native mavirus particles. (A) SDS/PAGE of flMCP turnover by MVP in vitro, performed in 50 mM SPG-NaOH pH 6.0, 1 mM TCEP, 5% (vol/vol) glycerol at 4 °C using 30 µM of each protein. flMCP, full-length MCP; L, protein ladder; MCPΔC, truncated MCP. Three C-terminal MCP fragments (MCPC1–C4) are indicated, but allocation of intermediate cleavage fragments was not possible based on the available data. (B) Scheme of MCP in vitro processing sites and fragments. N and C terminus and cleavage site residues refer to wild-type flMCP. (C) Native mavirus virion proteins. (C, Left) SDS/PAGE of mavirus particles. Indicated proteins were confirmed by MS PMF (i.e., significant Mascot score with P < 0.05). *No significant Mascot score for MV15 but 12 peptide mass matches. MV13N and MV13C refer to N- and C-terminal MV13 fragments, respectively. (C, Right) Immunoblot of MVP in mavirus virions. MVP, recombinant, purified protein (positive control). E. coli, cell lysate (negative control).