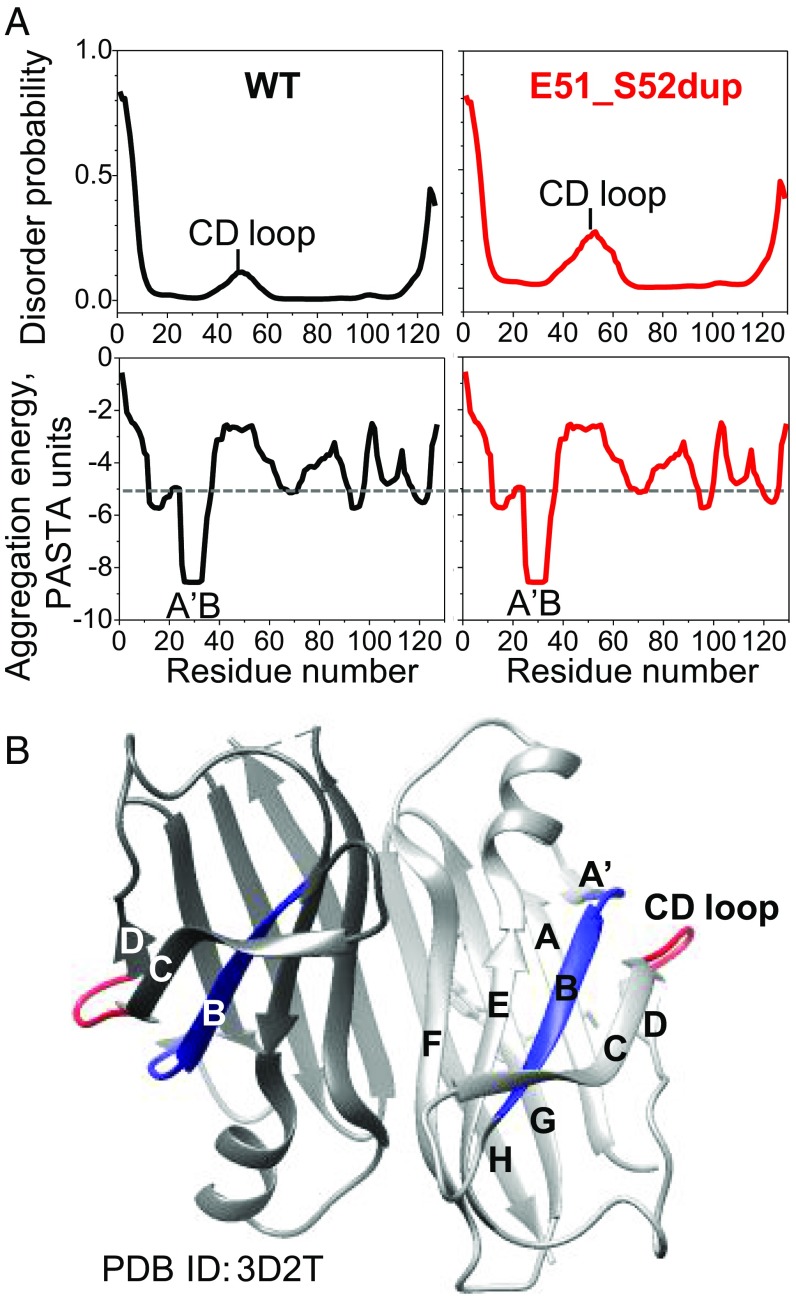
Fig. 8.
Effects of Glu51_Ser52dup mutation on the local protein structure predicted by bioinformatics methods. (A) Amino acid sequence analysis of WT and mutant TTR using the PASTA 2.0 server. (Top) In WT, increased disorder is predicted in residues 40–60 containing the CD loop, and is confirmed by hydrogen-deuterium exchange NMR (40, 42). The Glu51_Ser52dup mutation in the CD loop is predicted to further increase the disorder in this region. (Bottom) However, the mutation does not affect the amyloid-forming sequence propensity of TTR (shown as aggregation-free energy). Residues 25–34 from the A′B region are predicted to have the strongest amyloid-forming propensity in both WT and mutant TTR, with favorable (negative) aggregation-free energy exceeding the threshold of −5 PASTA units (dotted line; 1 unit = 1.92 kcal/mol). (B) X-ray crystal structure of WT TTR with bound diflunisal shows packing of the amyloidogenic segment (residues 25–34, in blue) from the A′B loop/strand, which is buried in the native structure, against the CD surface loop (residues 49–53, in red). Hence, the CD loop screens the amyloidogenic segment 25–34 from the solvent. Two dimer-forming molecules in ribbon representation are shown in different shades of gray. PDB, Protein Data Bank.