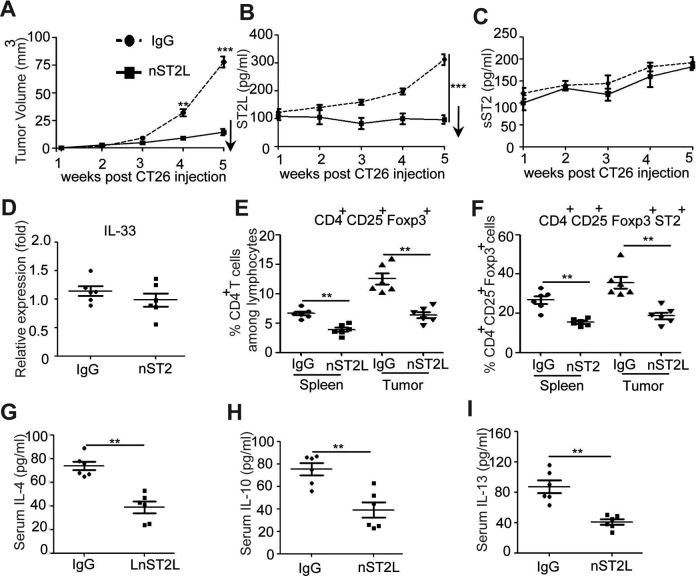
Figure 5.
Neutralization of ST2L reduced tumor size and antiinflammatory factor rabbit anti-mouse ST2L antibody or controls were administered to tumor-bearing mice. The dynamic tumor volume was observed (1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 weeks after ST2L neutralization) (A). The changes of sST2, ST2L, and IL-33 in the serum were detected by ELISA or qRT-PCR (B-D). Single-cell suspensions of the spleens or tumor tissues from control IgG group and ST2 neutralization group were prepared. Cells were stained with CD4-FITC, ST2L-APC, and CD25-PE-cyanine 7 and then intracellularly stained with PE-conjugated antibodies against Foxp3 for FACS analysis of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ (Treg) (E) and ST2L+CD4+ CD25+Foxp3+ (ST2L+Treg) (F). The serum from above mice was purified and detected the serum levels of Th2-related cytokine (IL-4, IL-10, and IL-13) by ELISA (F-G). (A-C, F-H) ***P < .001, Student t test; (G-I) **P < .01, ANOVA/SNK. IL indicates interleukin; sST2, soluble ST2; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; IgG, immunoglobulin G; PE, phycoerythrin; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; Treg, regulatory T; ANOVA, analysis of variance; SNK, Student-Newman-Keuls.