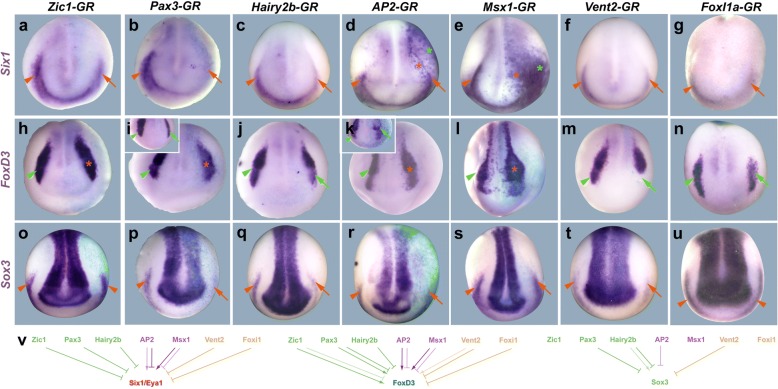
Fig. 2.
Role of early ectodermal TFs for PPE and NC formation. a–u Expression of PPE (Six1, Sox3), NC (FoxD3) and neural plate (Sox3) markers in dorsal views of neural plate stage Xenopus embryos after injection of mRNAs for hormone-inducible early ectodermal TF genes and dexamethasone activation from stage 11–12. Anterior is to the bottom. Control side is shown on the left and injected side on the right (as indicated by blue LacZ staining). Reductions (arrows) and increased or ectopic expression domains (asterisks) in the neural (green) and non-neural ectoderm (orange) compared with the control side (arrowheads) are indicated. Insets show alternative phenotypes. v Summary of regulatory interactions. Arrows indicate ability of TFs to promote expression of Six1/Eya1, FoxD3 or Sox3. Bars indicate ability of TF to repress Six1/Eya1, FoxD3 or PPE Sox3. Faint colors indicate less frequent phenotypes. See Additional file 1: Tables S4 and S5 for numbers