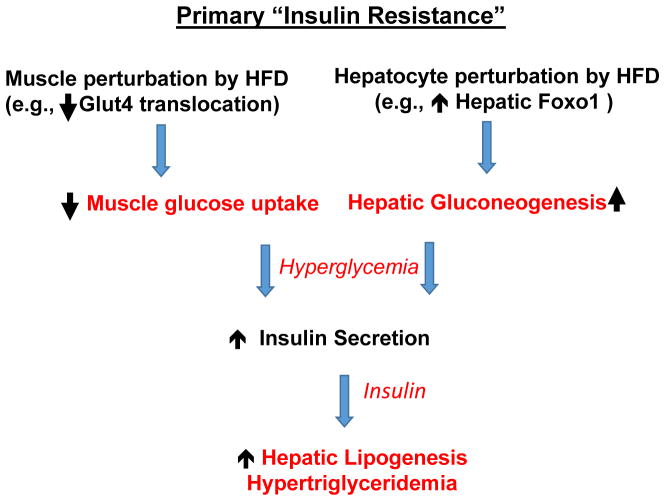
Figure 1. Plausible pathways whereby insulin resistance is the initiating response to high fat diet feeding and obesity to cause hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia.
High fat diets and overfeeding, either directly or indirectly through gut perturbations, disrupt downstream hepatocyte regulators of gluconeogenesis (e.g., increasing nuclear actions of the transcription factor Foxo1), causing increased hepatic glucose output, and disrupt Glut4 glucose transporter response to insulin. Inhibition of adipose insulin responsiveness to insulin also occurs (not shown). These disruptions cause hyperglycemia, which stimulates islet beta cells to secrete insulin, leading to hyperinsulinemia, which in turn activates hepatic lipogenesis and increased secretion of VLDL (hyperlipidemia).