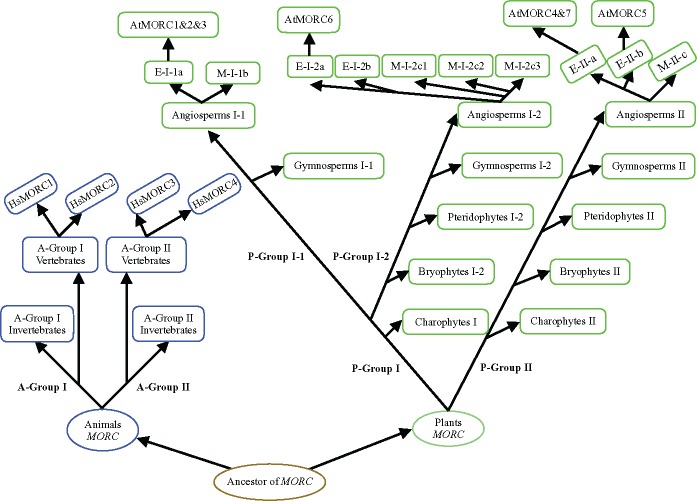
Fig. 6.
—A proposed model for the evolution of MORC genes in plants and animals. Based on sequence similarity, exon–intron organization and MORC domain, MORC genes in plants and animals can be divided into two major groups, respectively. The MORC gene is present in both plants and animals and its origin can be traced back to the common ancestor before the divergence of plants and animals. Animal MORCs underwent a gene duplication during the evolution of vertebrates in each subgroups and thus produced multiple gene copies in vertebrate lineages. Plant MORCs encountered several rounds of gene duplication events in the long-term evolutionary courses, eventually generating large-scale expansion in most species.