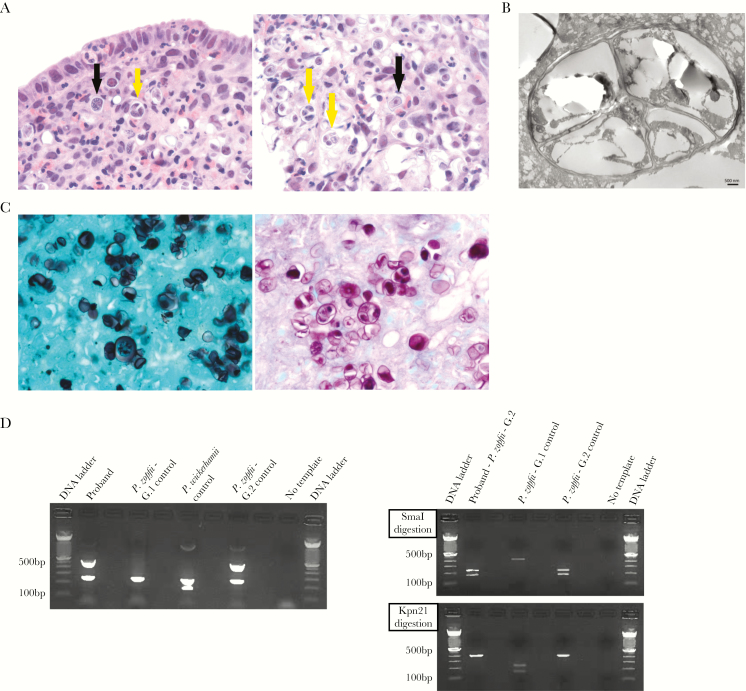
Figure 1.
Pathological and molecular characterization of Prototheca zopfii genotype 2 in proband’s colonic tissue. A, Hematoxylin-and-eosin stain shows numerous eosinophils and macrophages surrounding numerous round to oval algae (black arrows), with many of them undergoing endosporulation with multiple wedge-shaped endospores (yellow arrows) (left panel, 400×; right panel, 630×). B, Prototheca algae show characteristic endosporulation by transmission electron microscopy. Scale bar, 500 nm. C, Prototheca algae stain strongly with Grocott’s methenamine silver (left panel, 630×) and with periodic acid–Schiff stain (right panel, 630×). D, Prototheca multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay (left panel) shows Prototheca zopfii genotype 2 at 508 base pairs (bp), Prototheca zopfii genotype 1 at 216 bp, and Prototheca wickerhamii at 115 bp. Prototheca PCR–restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) assay distinguishes between P. zopfii genotype 1 and 2. The 450-bp PCR product was cut by the P. zopfii genotype 2–specific restriction enzyme SmaI, depicted in the right top panel, and not with the P .zopfii genotype 1–specific restriction enzyme Kpn21, shown in the right bottom panel. Abbreviations: bp, base pair; G.1, genotype 1; G.2, genotype 2; P. zopfii, Protheca zopfii; P. wickerhamii, Prototheca wickerhamii.