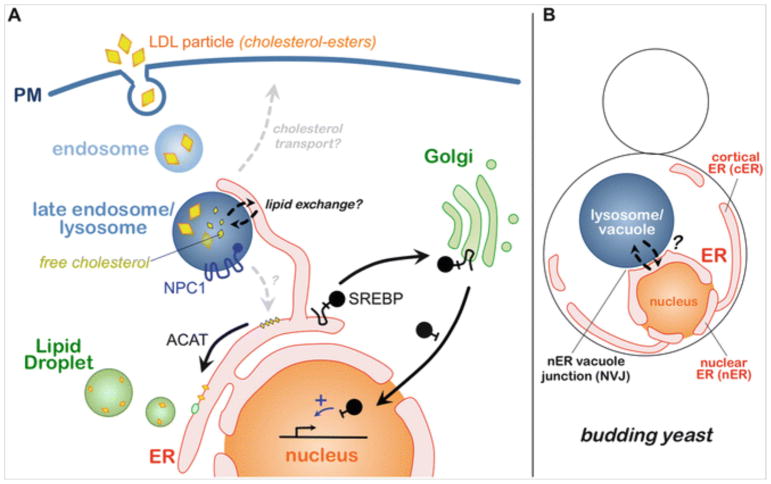
Fig. 10.1.
Trafficking pathways in human and yeast ER-endolysosomal systems. (a) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of LDL particles (containing sterol-esters) and their trafficking through the endosomal pathway to late endosomes/lysosomes, where cholesterol-esters within LDL particles are degraded into free cholesterol. Free cholesterol must then leave the lysosome lumen in an NPC1-dependent manner and traffic to the plasma membrane (PM) and/or the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). At the ER, the SREBP system senses local cholesterol levels. Low ER cholesterol induces the translocation and proteolytic cleavage of SREBP-2 at the Golgi, producing a soluble transcription factor which enters the nucleus. (b) The ER-endolysosomal system of budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The ER is partitioned into distal cortical ER (cER) and nuclear ER (nER), which makes direct contact with the vacuole/lysosome via the nER vacuole junction (NVJ)