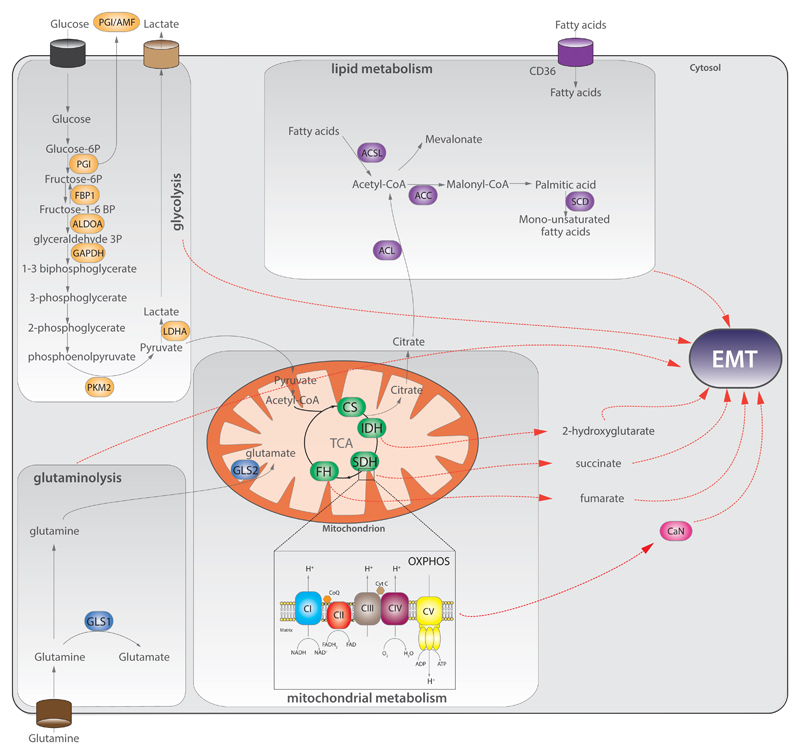
Fig.2. Metabolic genes control EMT.
Aberrant expression of metabolic enzymes of glycolysis (orange), lipid metabolism (purple), glutaminolysis (blue), mitochondrial metabolism (green), leads to EMT. Red dashed arrows indicate the link between specific metabolic pathway/metabolites and EMT. ACC=acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACL=ATP citrate lyase; ACSL=acetyl-CoA synthetase; ALDOA=aldolase A; CaN=calcineurin A; CI-CV=respiratory chain complexes I-V; CoQ=coenzyme Q; CS=citrate synthase; CytC=cytochrome C; FBP1=fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1; FH=fumarate hydratase; GAPDH=glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GLS=glutaminase; IDH=isocitrate dehydrogenase; LDHA=lactic dehydrogenase A; PGI =phosphoglucose isomerase; PKM2=pyruvate kinase M2; SCD=steroyl-CoA desaturase; SDH=succinate dehydrogenase.