Figure 1 |. The inflammatory reflex.
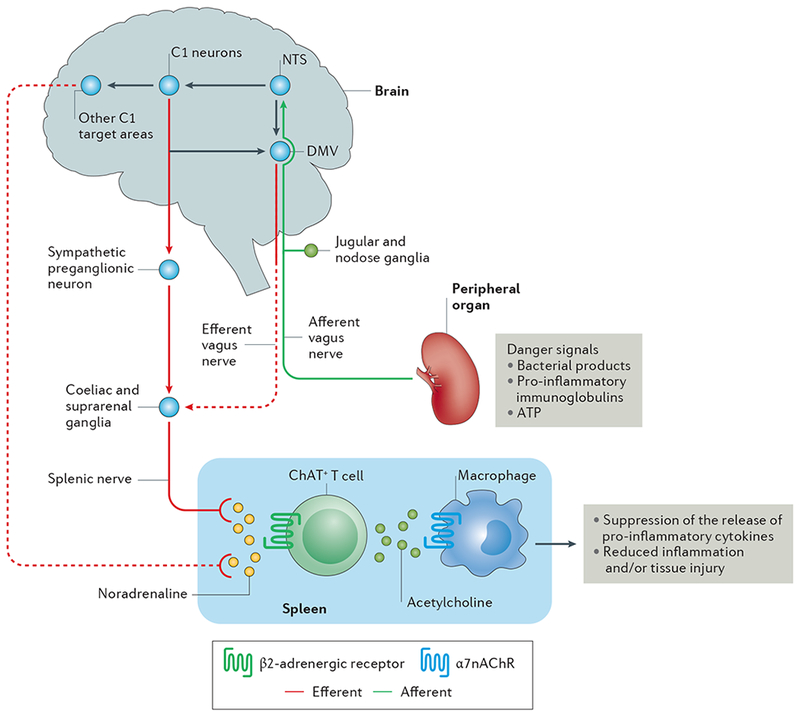
Afferent vagus nerve fibres transmit danger signals from peripheral organs to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS). This signalling leads to activation of the efferent vagus nerve arising in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV), and of the splenic nerve, leading to noradrenaline release in the spleen. This noradrenaline release activates choline acetyltransferase positive (ChAT+) T cells, which express β2-Activated ChAT + T cells release acetylcholine, which binds to α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (α7nAChRs) on macrophages, leading to suppression of the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced inflammation and/or tissue injury. In addition to activation of this cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP) by this vagal preganglionic efferent pathway, direct stimulation of brainstem C1 neurons (or indirect stimulation by a variety of physiological stressors) elicits activation of the CAP via a sympathetic efferent pathway76 that might involve C1 projections to sympathetic preganglionic neurons (which innervate sympathetic ganglia such as the coeliac and suprarenal ganglia) or other C1 projections in the brain that stimulate a sympathetic pathway. Dashed lines represent unconfirmed pathways, and solid lines represent confirmed pathways.
