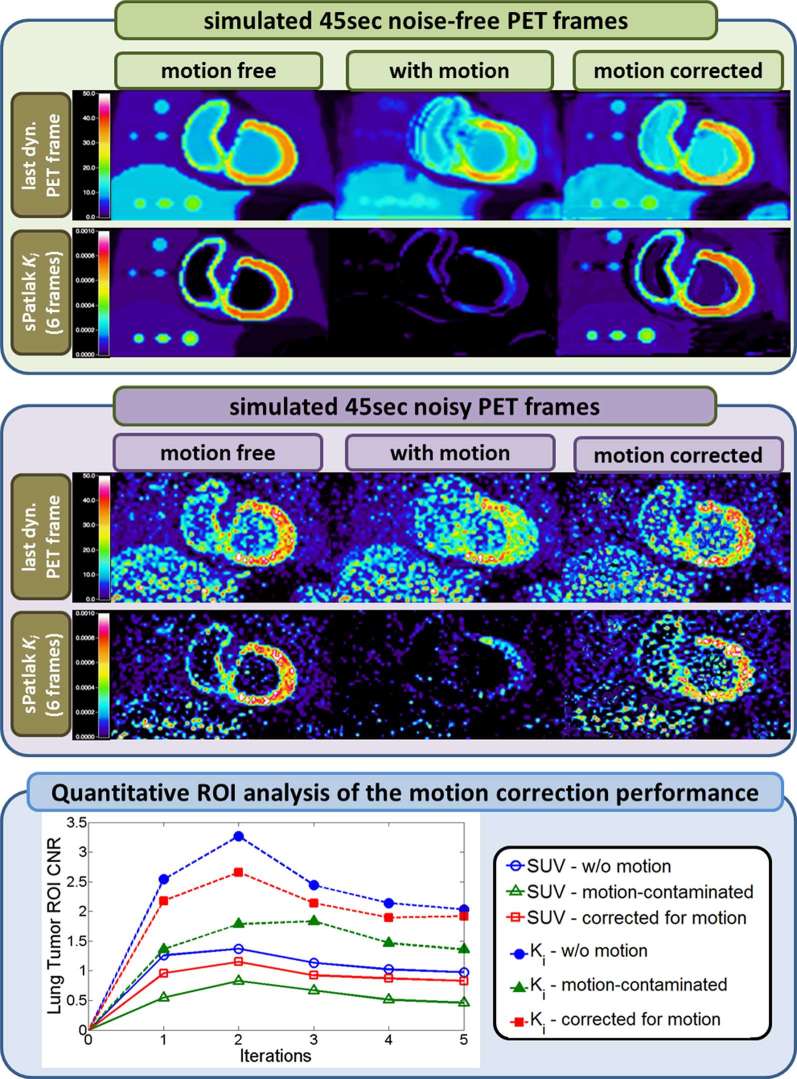
Figure 8.
(Top panel): Noise-free last dynamic PET SUV (top) and sPatlak images (bottom) corresponding to a simulated clinical WB dynamic cardiac PET acquisition. In all cases, motion-free, ground truth 4D data (first column) are used as a reference to compare against motion contaminated data estimated without motion correction (second column) and with nested RL-3D-MCIR correction (third column). All SUV PET images were reconstructed after 4 × 21 MLEM global iterations.Moreover, 10 nested RL subiterations were performed within each global iteration of the RL-3D-MCIR method. (Middle panel): Same dynamic PET (top) and sPatlak Ki images (bottom), after adding quantitative levels of Poisson noise on projection space, equivalent to 45 sec per bed frame and scaling to match the reported sensitivity performance of Siemens BiographTM mCT PET/CT scanner. (Bottom panel): CNRs for lung tumour as drawn on the PET SUV images (dotted curves) corresponding to the sixth dynamic frame and the respective sPatlak Ki images (continuous curves). The tumour CNR performance scores in the motion-compensated images with the proposed nested RL-3D-MCIR method (red squares) are evaluated against the simulated motion-free ground truth images (blue circles) and the uncorrected for motion images (green triangles ) of the SUV (empty markers) and Ki (filled markers) metrics. 4D, four-dimensional; MCIR, motion compensated image reconstruction; RL, Richardson-Lucy; 3D, three-dimensional.