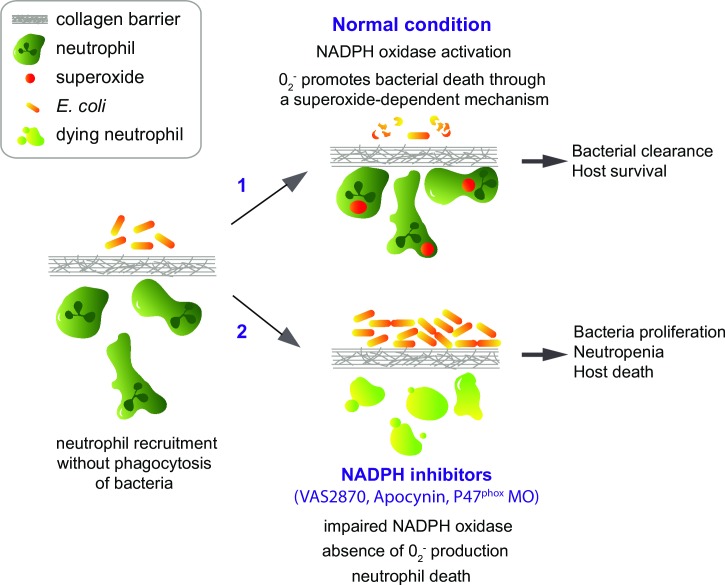
Fig 9. Graphical abstract of neutrophil defence against distant bacteria during notochord infection.
Low dose of E. coli infection in the notochord leads to the rapid recruitment of neutrophils to the notochord. During the first phase of infection, neutrophils cannot penetrate the collagen sheath and engulf bacteria. 1/ In normal condition, NOX activity in recruited neutrophils leads to the production of the ROS superoxide. Superoxide production participates in bacterial clearance without neutrophil-microbe physical contact through a yet unknown mechanism and results in host survival. 2/ Reducing the ROS superoxide using a drug that inhibits NADPH Oxidase assembly (VAS2870) or a drug that blocks NADPH Oxidase in the leukocytes (Apocynin) or using a p47phox morpholino results in bacteria growth in the notochord and host neutropenia and death.