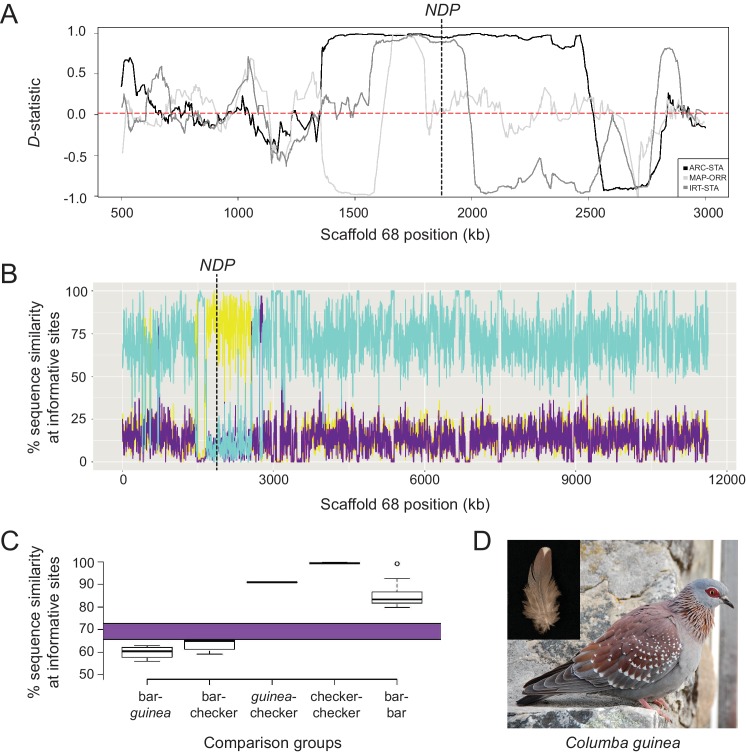
Figure 5. Signatures of introgression of the checker haplotype from C. guinea to C. livia.
(A) ABBA-BABA test with C. livia (bar), C. livia (checker), C. guinea, and C. palumbus shows elevated D-statistic in the Scaffold 68 candidate region. Three representative ABBA-BABA tests are shown and dashed red line marks the genome-wide mean D-statistic for 10 × 10 different combinations of bar and checker birds (ARC-STA, MAP-ORR, IRT-STA are shown, where ARC, MAP, and IRT are checker samples and STA and ORR are bar samples; see Methods). (B) HybridCheck shows pairwise sequence similarity across informative sites of a sequence triplet. A representative triplet of bar (Fer_VA), checker (ARC), and C. guinea comparison is shown. Blue trace shows sequence similarity between bar and checker, purple trace shows similarity between bar and C. guinea, and yellow trace shows sequence similarity between checker and C. guinea. (C) Expected (purple bar) and observed proportion of shared segregating sites out of 4261 total SNPs in the minimal haplotype region for different pairwise comparisons between and among 16 bar, 11 checker, and 1 C. guinea. (D) Speckled pigeon (Columba guinea). Photo courtesy of Kjeuring (CC BY 3.0 license, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/legalcode). Photo cropped from ‘speckled pigeon Columba guinea Table Mountain Cape Town,’ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speckled_pigeon#/media/File:Speckledpigeon.JPG. Inset feather image by the authors.