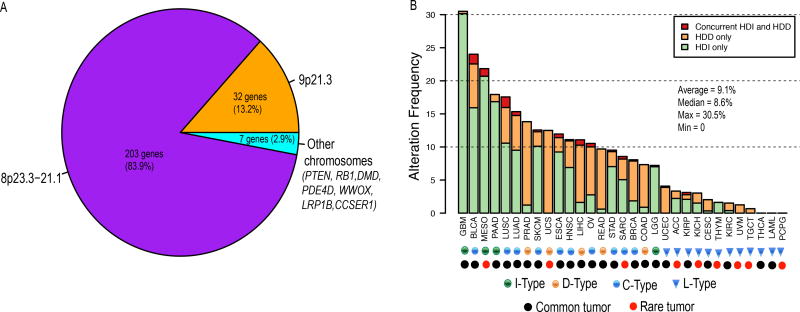
Figure 1. Genomic distribution of homozygously deleted genes and the deletion frequency of HDI/HDD in each tumor type.
(A) Genomic distribution of the 242 homozygously deleted genes identified. (B) Alteration frequency of HDI and HDD in 31 cancer types. Patients of each cancer type were divided into three groups: patients with HDI only (green), patients with HDD only (orange), and patients with concurrent HDI and HDD (red). The 31 cancers were classified into 4 types: L-type refers to cancer types with HDI/HDD frequencies less than 5% (blue triangle); I-type refers to cancer types in which HDI is the dominant alteration (green circle); D-type refers to cancer types in which HDD is the dominant alteration (orange circle); C-type refers to cancer types in which both HDI and HDD are prevalent (blue circle). Common and rare tumors are designated by TCGA and indicated using black and red circles, respectively. HDI, homozygous deletion of type-I interferons; HDD, homozygous deletion of defensin.