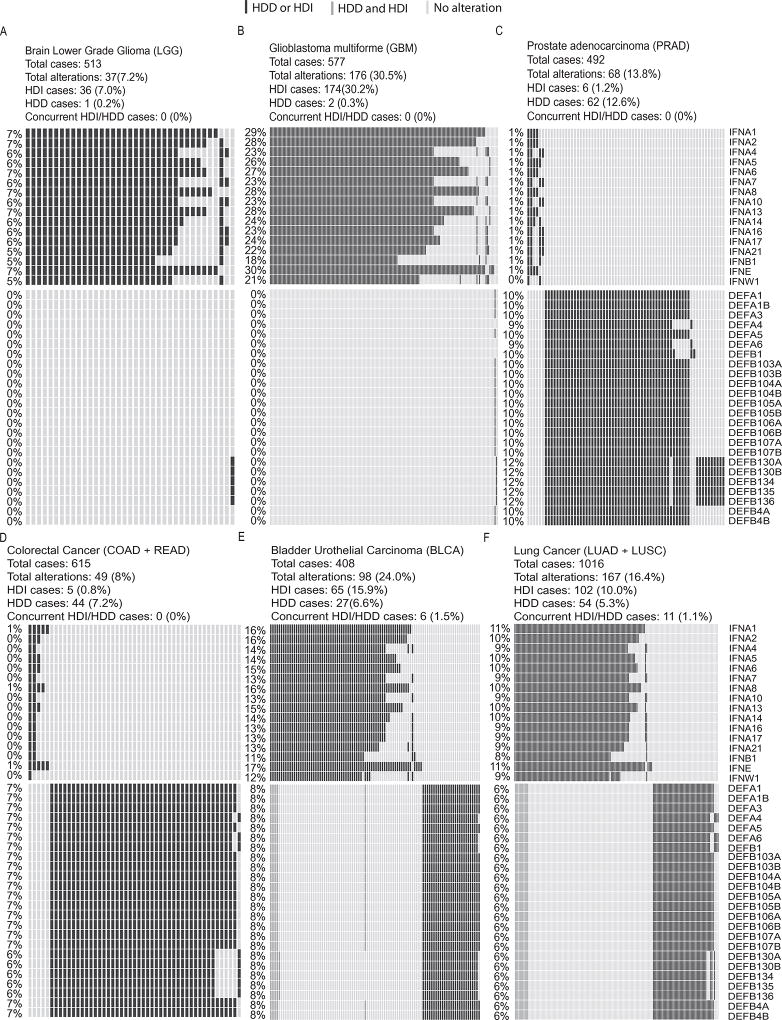
Figure 2. Homozygous deletions of interferon and defensin genes in six cancer types.
In each panel, rows represent genes and columns represent patients. Black bars indicate patients with HDD or HDI, grey bars indicate patients with concurrent HDD and HDI. Overall deletion frequency of each gene is listed on the left. (A–B) I-type cancers using brain lower grade glioma (LGG) and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) as examples. (C–D) D-type cancers using prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) and colorectal cancer as examples. Colorectal cancer is the combined cohort of colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) and rectum adenocarcinoma (READ). (E–F) C-type cancers using bladder urothelial carcinoma (BLCA) and lung cancer as examples. Lung cancer is the combined cohort of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). HDI, homozygous deletion of type-I interferons; HDD, homozygous deletion of defensin.