Figure 8.
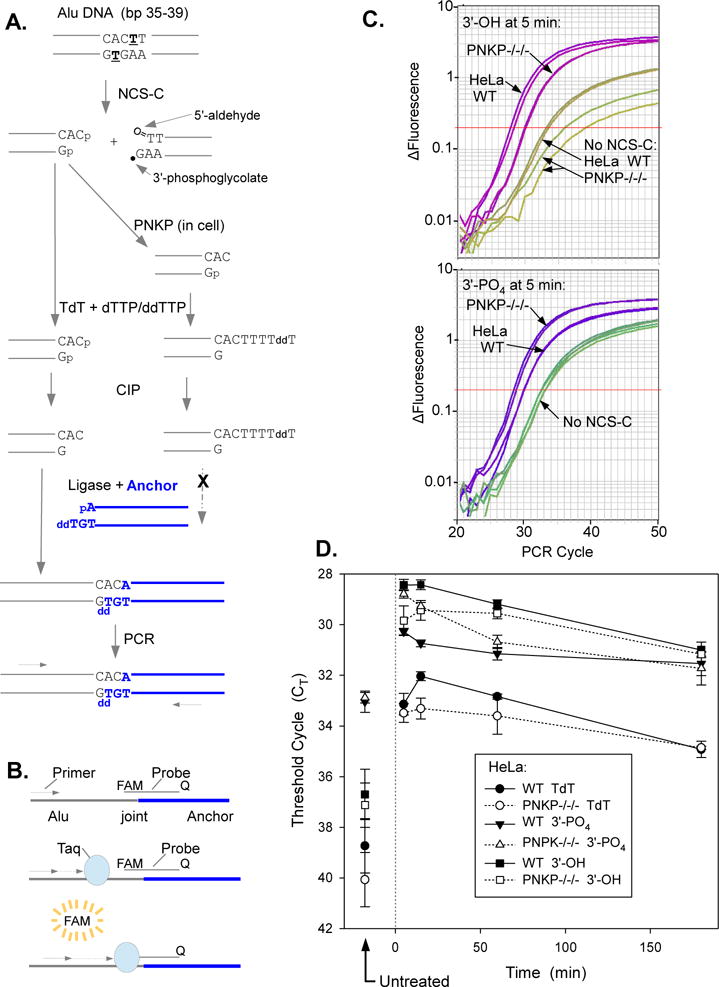
Deficiency in 3′-dephosphorylation of NCS-C-induced DSBs in PNKP−/−/− HeLa cells as determined by LMPCR. Cells were treated with 5 μM NCS-C and incubated at 37°C for 5-180 min. DNA was isolated and 3′ termini of DSBs were assessed by ligation-mediated PCR. A. Experimental scheme. NCS-C induces DSBs preferentially at AGT●ACT sequences, including at bp 36-38 of the human Alu repeat. The left-hand DSB end has an overhanging 3′-phosphate. To quantify these phosphate ends, any existing 3′-hydroxyl ends are first blocked by tailing with TdT and dTTP/ddTTP. The 3′-phosphates are then removed with CIP and the resulting 3′-hydroxyl DSB ends are ligated to an anchor and quantitated by ligation-mediated real-time PCR. To quantitate 3′-hydroxyl DBSs formed in the cell by PNKP, DNA from NCS-C-treated cells is subjected to LMPCR without any prior enzyme treatments, B. Principle of Taqman PCR. As PCR product accumulates, the fluorescent probe binds to the Alu/anchor junction after each denaturation cycle and the fluorophore is released by the 5′→3′ exonuclease of Taq polymerase as it replicates the product, resulting in an exponential increase in fluorescence as a function of cycle number. C. LMPCR amplification profiles from a representative experiment, showing more 3′-phosphate DSBs and fewer 3′-hydroxyl DSBs in PNKP−/−/− than in WT HeLa cells. Amplification profiles from duplicate PCR reactions are shown for each condition. D. Time course for formation and disappearance of 3′-phosphate and 3′-hydroxyl NCS-induced DSBs, as determined by LMPCR of cell DNA treated with TdT plus CIP or neither enzyme, respectively. CT values for DNA treated with TdT only are also shown. Error bars show the mean ± SEM from 4 independent experiments.
