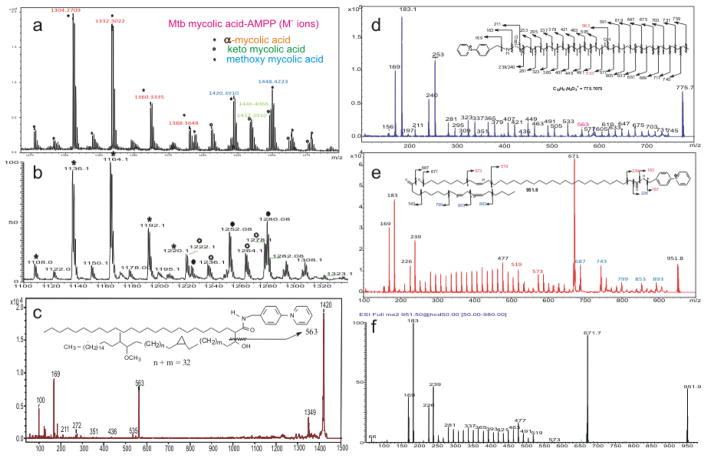
Figure 5.
(a) The MALDI TOF (reflectron) spectrum of the M+ ions of M. tuberculosis (bovine) mycolic acid-AMPP derivative; and (b) the corresponding ESI mass spectrum seen as the [M–H] − ions of the underivatized mycolic acid obtained with an linear ion trap instrument. Panel c shows the MALDI LIFT TOF-TOF spectrum of a methoxy mycolic acid-AMPP species of m/z 1420, containing a α-tetraeicosanoyl (C24) chain. Panel d shows the LIFT TOF-TOF spectrum of the ions of C-40 HPA-AMPP at m/z 775, consisting of multiple methyl branches and hydroxyl side chain; and the fragmentation scheme (inset). Panel e and Panel f show the MS2 spectra of the M+ ions of O-linoleoyl ω-hydroxytetratriacontenoic acid (O-Δ9,12-18:2-ωhΔ25 34:1)-AMPP at m/z 951 obtained with LIFT TOF-TOF and LIT/HCD, respectively. The structural information of the Δ9,12-18:2 terminus is missing in Figure 5f, due to absence of ions from CRF losses of CnH2n+2 residues of the aliphatic tail that requires high collision energy. Please note that a cis configuration in inset is drawn, however, distinction between cis and trans isomers cannot be made by tandem mass spectrometry.