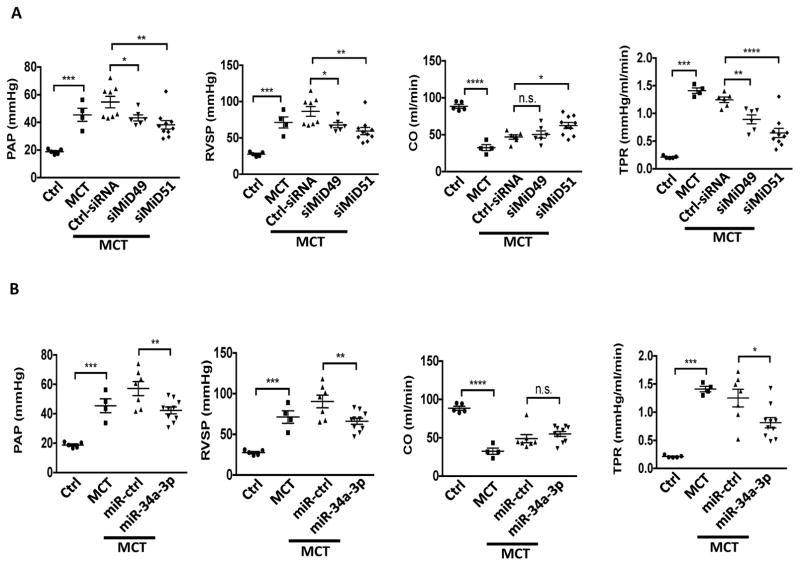
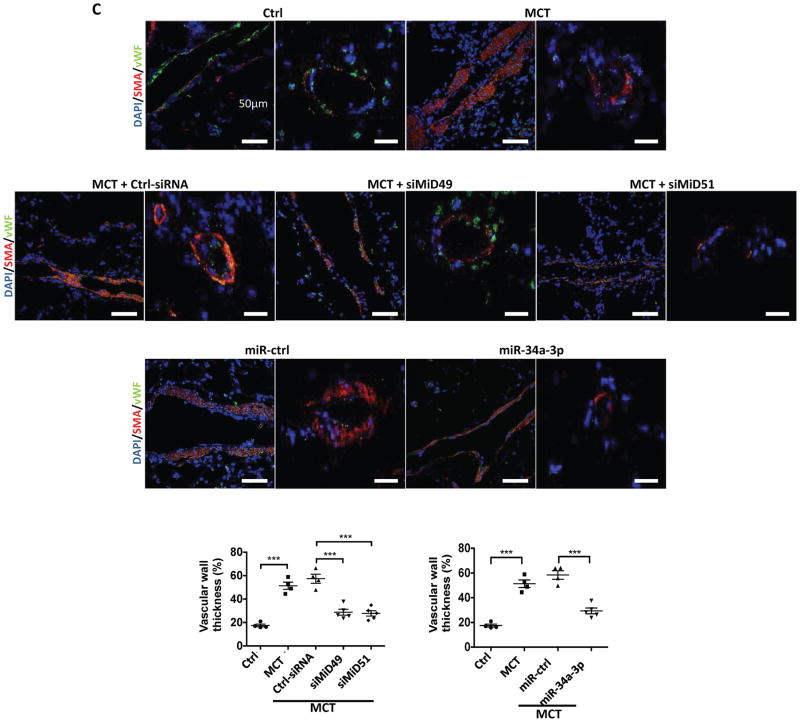
Fig. 6. Demonstration of the therapeutic relevance of the miR-34a-3p-MiD pathway in preclinical model.
(A) Nebulized siMiDs regress monocrotaline-induced PAH (MCT PAH). Compared to control rats, MCT PAH rats had elevated PAP, RVSP and decreased CO, as determine by closed-chest right heart catheterization. siMiD49 and siMiD51 treatments were effective in decreasing PAP, RVSP and increasing CO resulting in significant decrease of TPR (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; One way ANOVA, n=4–10/group).
(B) Augmenting miR-34a-3p regresses MCT PAH. Decreased PAP, RVSP and increased CO resulting in significant decrease of TPR (n.s., not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; One-way ANOVA, n=4–10/group).
(C) Representative images of longitudinal and cross sections of small pulmonary arteries and summary data indicating the regression of PAH caused by siMiD49 or siMiD51 or by miR-34a-3p mimic was associated with a decrease in the wall thickness in MCT PAH rats. Regression of PAH was assessed by measuring % of wall thickness by immunofluorescence staining of smooth muscle actin (SMA) and von Willebrand Factor (vWF) (blue: DAPI, red: SMA, green: vWF) (***P < 0.001; One-way ANOVA, n=4–5/group). Scale bar: 50μm.