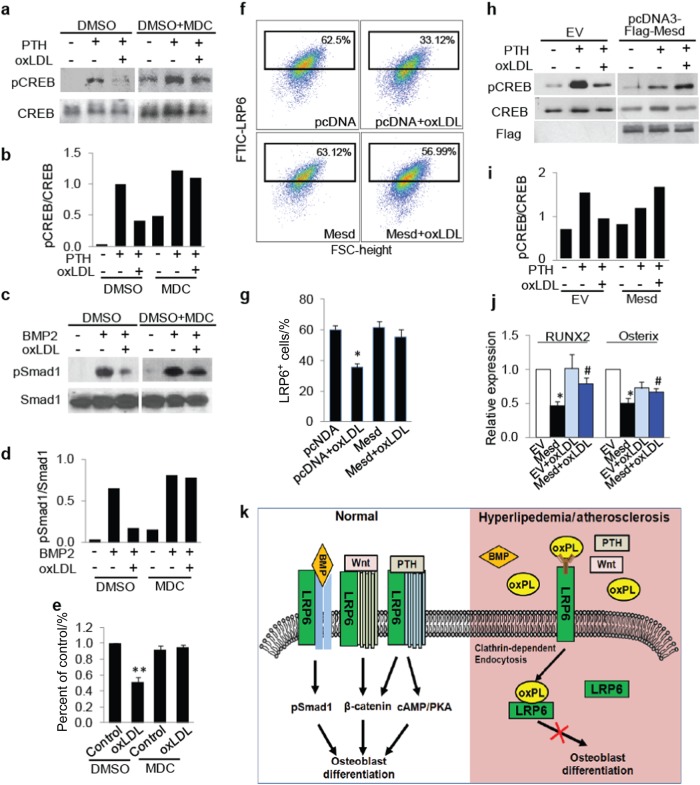
Fig. 7.
Manipulating cell surface LRP6 level antagonizes the adverse effect of oxPLs on MSCs. a, b MSCs were treated with vehicle or 50 nmol·L-1 PTH in the absence or presence of 20 μg·mL-1l oxLDL and/or 100 μmol·L-1 MDC for 1 h. Protein extracts of the cells were subjected to Western blot using antibodies to phosphorylated CREB or total CREB (a). Relative quantification for phosphor-CREB expression normalized with respect to total CREB (b). c, d MSCs were treated with 50 ng·mL-1 BMP2 in the absence or presence of 20 μg·mL-1 oxLDL and/or 100 μmol·L-1 MDC for 1 h. Protein extracts of the cells were subjected to Western blot using antibodies to phosphorylated Smad1 or total Smad1 (c). Relative quantification for phosphor-Smad1 expression normalized with respect to total Smad1 (d). e MSCs were cultured in osteogenic medium with 20 μg/ml oxLDL and/or 100 μmol·L-1 MDC. Cells were fixed and stained with Alizarin Red S 21 days after treatment. Relative intensity of the Alizarin Re·d staining in each group was normalized to the level of control group. f, g MSCs were transfected with pcDNA3 or pcDNA3-Mesd plasmids and treated with 20 μg·mL-1 oxLDL for 30 min. Representative images of the flow cytometry analysis (f) and the percentage of LRP6+ cells (g). n = 5, data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, vs. pcDNA group; #P < 0.05, vs. pcDNA + oxLDL group, as determined by Student’s t-tests. h, i MSCs were transfected with pcDNA3 (EV) or pcDNA3-Mesd plasmids and treated with 50 nmol·L-1 PTH and/or 20 μg/ml oxLDL for 1 h. Protein extracts of the cells were subjected to Western blot using antibodies to phosphorylated CREB or total CREB (h). Relative quantification for phosphor-CREB express·ion normalized with respect to total CREB (i). j MSCs were transfected with pcDNA3 (EV) or pcDNA3-Mesd plasmids and incubated with osteogenic medium with or without 20 μg·mL-1 oxLDL for 7 days. mRNA expressions of RUNX2 and osterix were detected by Real-time PCR analysis. n = 5, data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.01 vs. EV group; #p < 0.05 vs. EV + oxLDL group, as determined by Student’s t-tests. k Schematic model illustrating the role of LRP6 in oxPLs-induced MSC functional loss. Cell surface LRP6 in MSCs can be recruited by the receptors of Wnts, PTH, and BMPs and mediates their signaling activation for osteoblast differentiation (left panel). During hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis, high level of oxPLs in bone marrow directly bind cell surface LRP6 and induce rapid LRP6 endocytosis, leading to blunted responses of MSCs to these osteogenic factors (right panel)