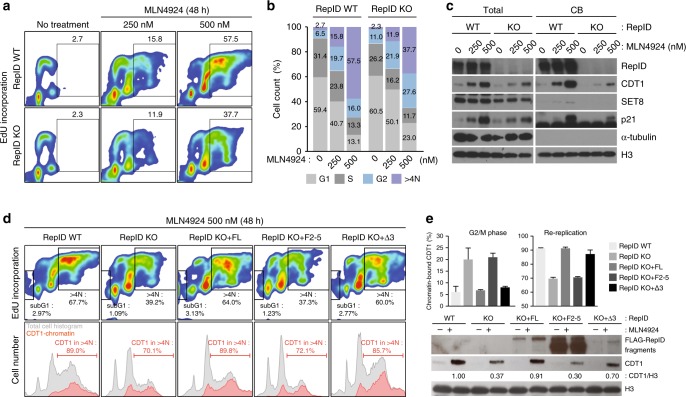
Fig. 4.
RepID depletion confers resistance to the neddylation inhibitor MLN4924. a U2OS WT or RepID KO cells were incubated with or without 250 and 500 nM MLN4924 for 2 days. Cells were labeled with EdU for 30 min prior to collection and analyzed by FACS. Percentage of re-replicating cells is indicated. b Bar chart depicting the cell cycle distribution of cells collected in a. c Chromatin-bound (CB) proteins isolated as in a and analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against CRL4 substrates including CDT1, SET8, and p21. d WT, RepID KO U2OS cells and RepID KO U2OS cells stably transfected with RepID variants were treated with 500 nM MLN4924 for 2 days and labeled with EdU for 30 min prior to collection and analyzed by FACS. Percentage of subG1 and re-replicating cells are indicated (upper panels). Percentages of chromatin-bound CDT1 in re-replicating cells are indicated (red, bottom panel). e Graphs depicting the percentage of chromatin-bound CDT1 in cells in G2/M phase (left panel) or in re-replicating cells (right panel). The intensity of chromatin-bound CDT1 in specific cell cycle fractionated cells isolated as in d was measured by immunoblotting (bottom panel). The numbers under the panel represent the ratios of CDT1 intensities relative to the intensity of the signal in MLN4924-treated RepID WT cells after normalization with histone H3 from three independent experiments