FIGURE 6.
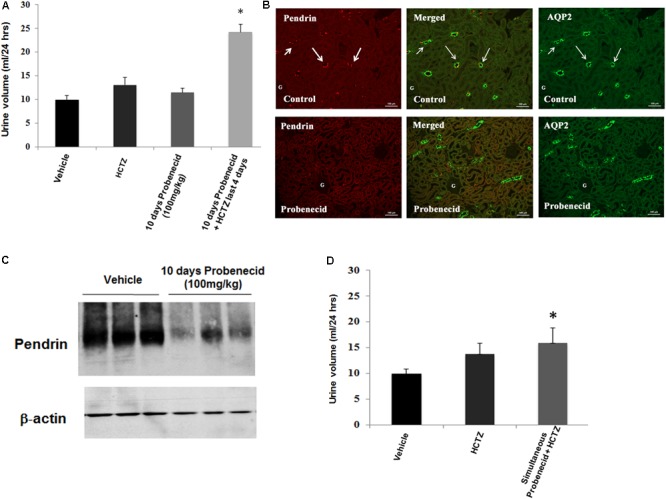
Effect of probenecid at 100 mg/kg, with or without HCTZ, on urine volume and pendrin expression. (A) Effect of probenecid pre-treatment on HCTZ-induced diuresis. Data depicts urine output in rats pre-treated with Probenecid at 100 mg/kg for 6 days followed by co-treatment with 100 mg/kg Probenecid and HCTZ for an additional 4 days. When adjusted for body weight, the results, expressed as urine volume/24 h/body weight were as follows: Vehicle (0.05 ± 0.004, n = 12) vs. probencid (100 mg) ± HCTZ (0.11 ± 0.008, n = 7); p = 0.000001. ∗ denotes significance between Vehicle vs. Probenecid/HCTZ co-treatment. (B) Double immunofluorescence labeling with pendrin and AQP-2. Top panel: Control. AQP2 (right) and Pendrin (left), with merged image in the middle panel. Bottom: probenecid. Effect of 100 mg/kg of probenecid for 10 days on AQP2 (right) and pendrin (left), with merged images in middle. (C) Western blot analysis of pendrin in probenecid pre-treated rats at 100 mg/kg/day. Western blots indicate significant reduction in the expression of pendrin in rats pre-treated with probenecid at 100 mg/kg/day for 6 days. Vehicle (1.01 ± 0.02, n = 3) vs. 10 days probenecid (100 mg/kg) (0.56 ± 0.11, n = 3; p = 0.02). (D) Effect of simultaneous treatment of probenecid and HCTZ without probenecid priming on urine volume. The magnitude of daily urine volume in simultaneous co-treatment of 100 mg/kg/day of probenecid and HCTZ without probenecid priming was not significantly different when compared to HCTZ-treated animals but was significant vs. vehicle treated rats. When adjusted for body weight, the results, expressed as urine volume/24 h/body weight were as follows: HCTZ (0.06 ± 0.01, n = 5) vs. Simultaneous probenecid + HCTZ (0.07 ± 0.01, n = 4; p = 0.42). ∗ denotes significance between Vehicle and Simultaneous treatment of Probenecid/HCTZ. However, there was no significant difference between simultaneous treatment of Probenecid/HCTZ and HCTZ alone.
