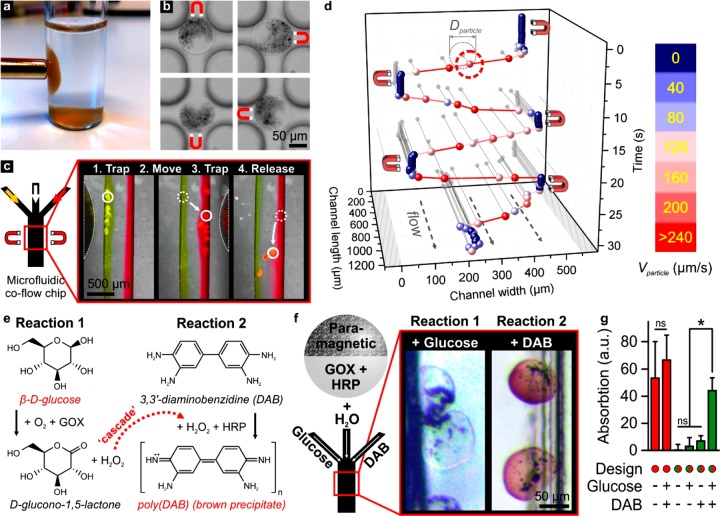
Figure 3.
Multifunctional Janus microparticles as magnetically steerable enzymatic microreactors. Using a magnetic field, Janus microparticles with a paramagnetic compartment could be (a) moved and (b) oriented within a static carrier liquid. (c, d) The same particles could also be trapped and moved with micrometer precision within a laminar coflowing liquid. (e) The enzymes glucose oxidase (GOX) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) can together drive a cascade reaction via the sequential enzymatic production and reaction of H2O2. In the presence of β-d-glucose and of 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB), a successful cascade reaction is indicated by the formation of poly(DAB), which appears as a brown precipitate. (f) Janus microparticles with paramagnetic and GOX/HRP compartments could be leveraged as steerable microreactors to facilitate a multienzymatic cascade reaction within a laminar coflow of β-d-glucose, H2O, and DAB. (g) Compartmentalization of the brown paramagnetic particles and the enzymes was key to enable accurate quantification of the enzymatic cascade reaction product using absorption spectrophotometry. Furthermore, spectrophotometric analysis of various reagent combinations confirmed that both β-d-glucose and DAB were essential to complete the cascade reaction. “ns” indicates no significance. * indicates significance with p < 0.01.