Table 1. Ligand screening and reaction optimization a .
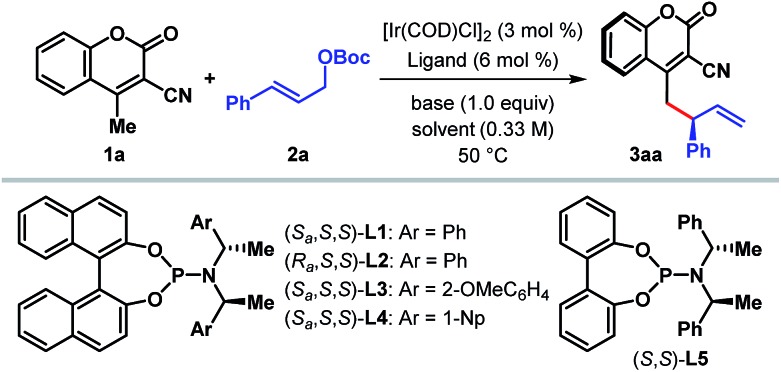
| ||||||
| Entry | Ligand | Solvent | Base | t [h] | Yield b [%] | er c |
| 1 | L1 | DCE | — | 48 | (22) | 92.5 : 7.5 |
| 2 | L1 | DCE | Cs2CO3 | 48 | <5 | n.d. |
| 3 | L1 | DCE | DBU | 48 | <5 | n.d. |
| 4 | L1 | DCE | i-Pr2NEt | 48 | 72 | 96 : 4 |
| 5 | L1 | DCE | Et3N | 48 | 74 | 97 : 3 |
| 6 | L1 | DCE | i-Pr2NH | 48 | 76 | 97 : 3 |
| 7 | L1 | DCE | DABCO | 48 | 84 | 97.5 : 2.5 |
| 8 | L2 | DCE | DABCO | 48 | <5 | n.d. |
| 9 | L3 | DCE | DABCO | 48 | 11 | 98 : 2 |
| 10 | L4 | DCE | DABCO | 48 | <5 | n.d. |
| 11 | L5 | DCE | DABCO | 48 | 28 | 92 : 8 |
| 12 | L1 | THF | DABCO | 48 | 11 | 96 : 4 |
| 13 | L1 | CHCl3 | DABCO | 48 | 67 | 97 : 3 |
| 14 | L1 | CH2Cl2 | DABCO | 36 | 88 (86) | 98 : 2 |
aReaction conditions: 3 mol% [Ir(COD)Cl]2, 6 mol% ligand, 0.24 mmol of 1a, 0.2 mmol of 2a and 0.2 mmol of base in 0.6 mL solvent. The catalyst was prepared via n-PrNH2 activation.
bYields were determined by 1H-NMR spectroscopy with mesitylene as the internal standard. Isolated yields are given in the parentheses.
cThe enantiomeric ratio (er) was determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase; n.d. = not determined. DCE = 1,2-dichloroethane.
