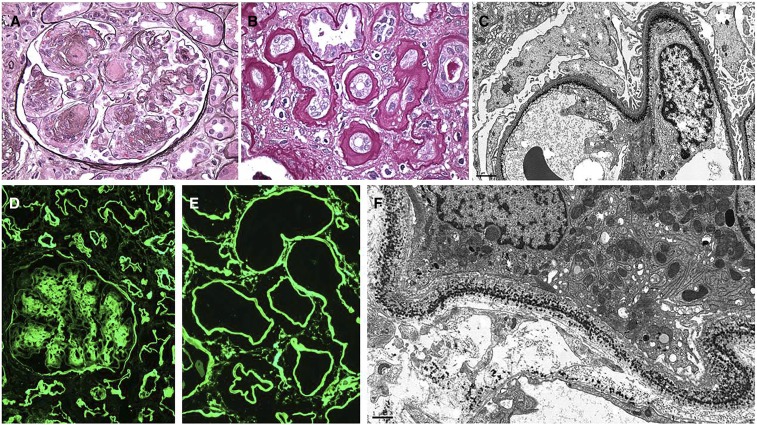
Figure 4.
MIDD due to κ–LCDD. A 95-year-old man presents with AKI, nephrotic syndrome, and serum creatinine 2.7 mg/dl (increased from baseline 1.4 mg/dl 4 months prior) with lower extremity edema, urine protein 7 g/d, and serum protein electrophoresis with immunofixation showing elevated monoclonal κ-light chains. Renal biopsy shows the following. (A) Nodular sclerosing glomerulopathy with nodular mesangial expansion by partially silver-negative material associated with foci of circumferential mesangial interposition (Jones methenamine silver). Original magnification, ×400. (B) Thick ribbon-like periodic acid–Schiff (PAS)-positive deposits involving the tubular basement membranes (PAS). Original magnification, ×400. (C) Electron microscopic demonstration of finely granular punctate powdery deposits along the lamina rara interna of the glomerular capillary walls. Original magnification, ×8000. (D) Immunofluorescence staining for κ-light chain only distributed in the mesangial nodules, with weak linear staining of glomerular basement membranes and stronger linear staining of Bowman’s capsule and the tubular basement membranes. Original magnification, ×200. (E) Intense diffuse linear immunofluorescence staining for κ-light chain in the distribution of the tubular basement membranes associated with sparse interstitial positivity. Original magnification, ×400. (F) Punctate peppery deposits involving the tubular basement membrane and to a lesser extent, the adjacent interstitial capillary basement membrane (electron micrograph). Original magnification, ×10,000.