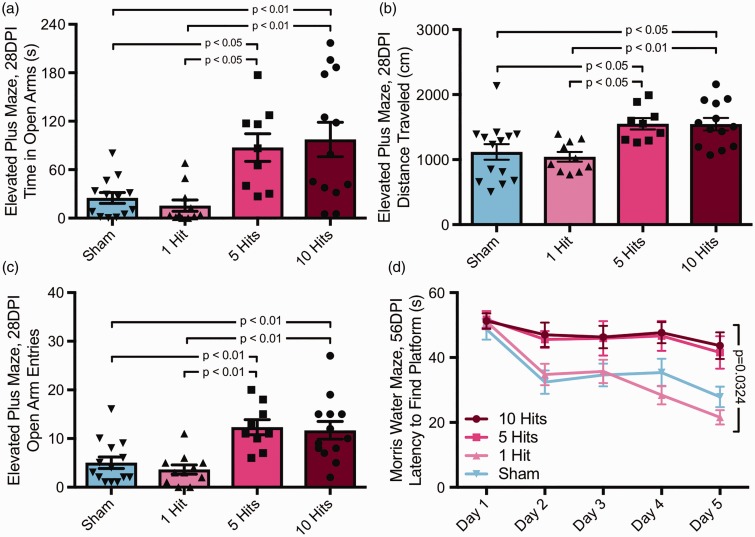
Figure 4.
rmCHI alters cognitive function at 1 and 2 months postinjury. Following 0, 1, 5, or 10 rmCHIs, mice were tested on the elevated plus maze at 28 DPI (1 month) and the Morris water maze at 56 DPI (2 months). (a) rmCHI resulted in changes to performance on the elevated plus maze. Mice with 5 or 10 hits spent more time in the open arms compared with sham or 1-hit mice (one-way ANOVA), F(3, 42) = 8.301, p = .0002, and (b) rmCHI mice also traveled more distance during the task (one-way ANOVA), F(3, 42) = 6.800, p = .0008, demonstrating hyperactivity and no prolonged motor deficits. (c) In addition, mice with 5 or 10 hits exhibited more open arm entries than sham or 1-hit mice (one-way ANOVA), F(3, 42) = 9.327, p < .0001. (d) 2 months postinjury, mice were tested over 5 days on the Morris water maze. rmCHI mice that received either 5 or 10 hits were impaired in the ability to learn the location of the hidden platform (two-way ANOVA), F(12, 172) = 1.943, p = .0324 interaction. The p values on graphs represent Tukey post hoc differences.
rmCHI = repeated mild closed head injury; DPI = days postinjury; ANOVA = analysis of variance.