Figure 6.
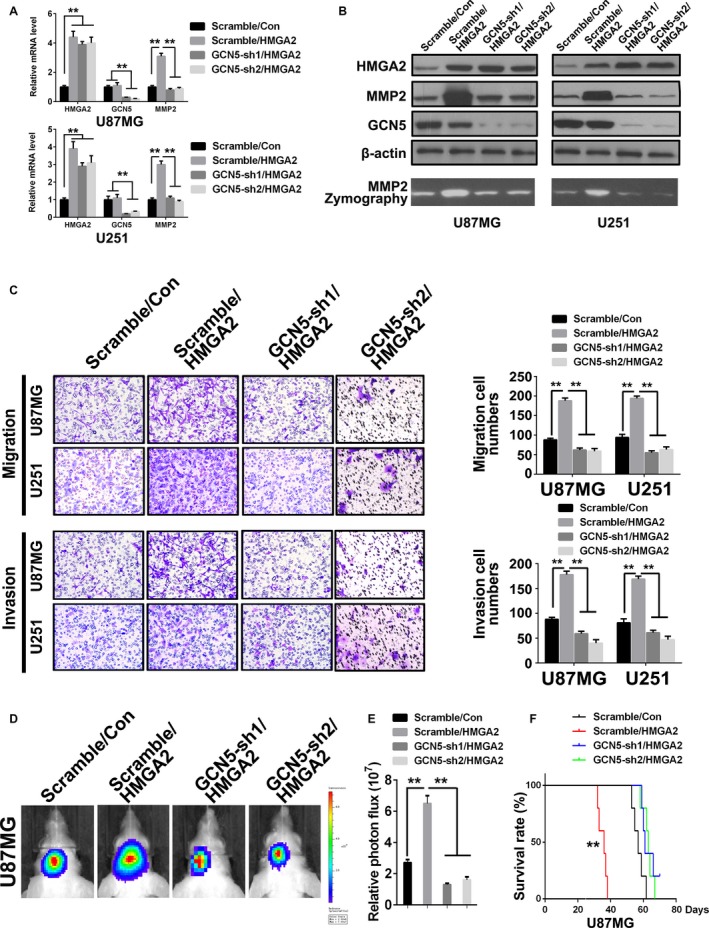
HMGA2 facilitates GBM cell malignancy via GCN5. A, qPCR analyses of the mRNA level of HMGA2, GCN5, and MMP2 in the U87MG and U251 cells of control (Scramble/Con), HMGA2 overexpression (Scramble/HMGA2), and HMGA2 overexpression with GCN5 knockdown (GCN5‐sh1/HMGA2 and GCN5‐sh2/HMGA2) groups. n = 3, **, P < .01. B, The protein levels of HMGA2, GCN5, and MMP2 in the aforementioned cells in (A). Gelatin zymography analyses of the activity of MMP2 in the aforementioned cells in (A). C, Transwell assay was performed to measure the migration and invasion ability of the aforementioned cells in (A). n = 3, **, P < .01. D, Six‐week‐old NOD‐SCID mice were orthotopically inoculated with U87MG cells infected with lentiviruses carrying an empty vector plus scramble shRNA (Scramble/Con) or ectopic HMGA2 plus scramble shRNA (Scramble/HMGA2) or GCN5 shRNA (GCN5‐sh1/HMGA2, GCN5‐sh2/HMGA2), n = 5/group. E, Tumors were quantified using IVIS luminescence image system. n = 5, **, P < .01. F, Kaplan‐Meier survival test result for in vivo tumor transplant assay. The survival in the Scramble/HMGA2 group was significantly shorter than that in other groups. n = 5, **, P < .01. The data in (A, C, E) are given in mean ± SD
