Figure 3.
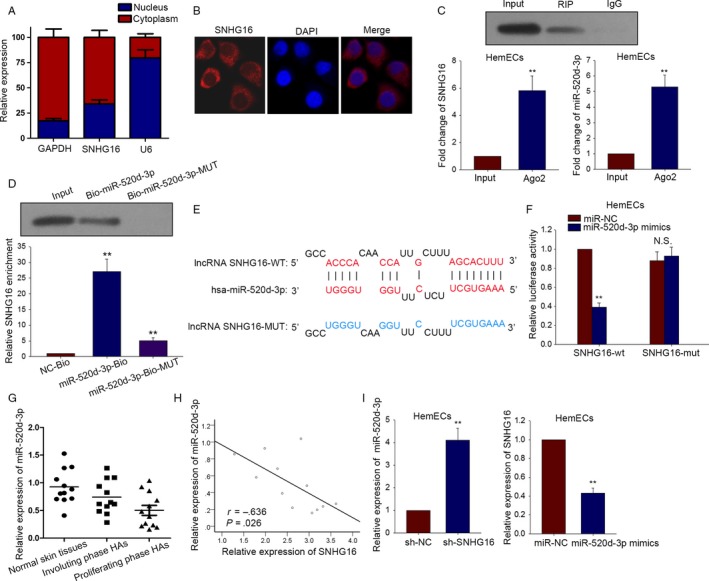
SNHG16 can bind with miR‐520d‐3p in HemECs. A, Subcellular fractionation assay examined the localization of SNHG16 in HemECs cell. B, RNA FISH was performed to probe the localization of SNHG16 in HemECs cell. C, RIP assay was conducted in HemECs with antibodies against Ago2 to find the combination between SNHG16 and miR‐520d‐3p. D, The binding relation between SNHG16 and miR‐520d‐3p was verified by pull‐down assay. E, The binding sites were obtained between two types of SNHG16 (wild type and mutant type) and miR‐520d‐3p. F, Dual‐luciferase assay was also performed to confirm the interaction between SNHG16 and miR‐520d‐3p. G, The expression of miR‐520d‐3p was tested in three different types of tissues. H, The correlation between SNHG16 and miR‐520d‐3p was proved by Spearman's correlation method. I, qRT‐PCR examined the effect of silenced SNHG16 on miR‐520d‐3p expression and the impact overexpressed miR‐520d‐3p on SNHG16 expression. Data were acquired from multiple experiments for mean ± SD. *P < .05, **P < .01 compared with controls
