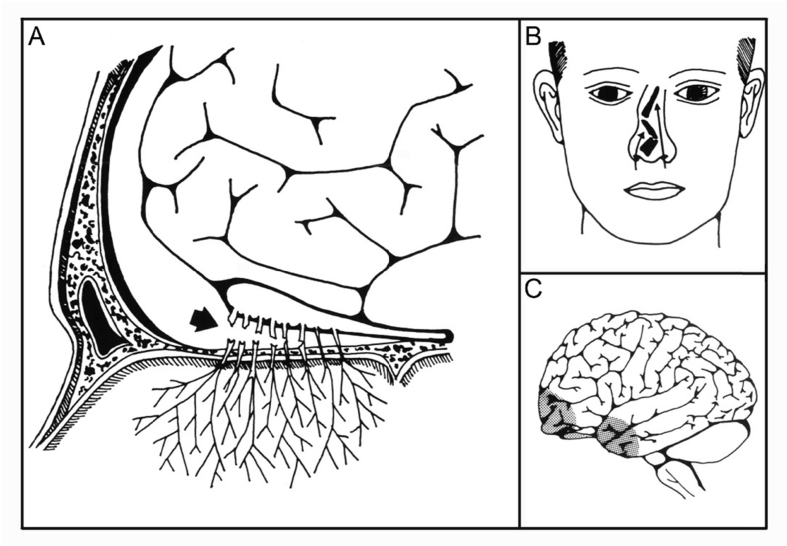
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms underlying olfactory dysfunction following traumatic head injury. (A) direct shearing or tearing of olfactory nerve fibers at the cribriform plate, (B) sinonasal tract disruption, and (C) focal contusion or hemorrhage within the olfactory cortex. Adapted from Costanzo and Zasler12 with permission, copyright, Walters Kluwer.