Figure 3.
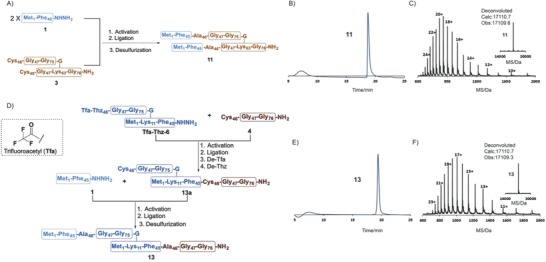
Synthesis of K63‐diUb 10: A) Overall synthetic route; B) analytical HPLC chromatogram of purified 10; C) observed ESI‐MS spectrum of purified 11 (24+, 713.9; 22+, 778.7; 20+, 856.5; 18+, 951.5; 16+, 1070.4; 14+, 1223.1; 12+, 1426.8; and 10+, 1712.0); inset: deconvoluted ESI‐MS spectrum of 11, observed mass = 17 109.6 Da, calculated mass = 17 110.7 Da, average isotopes). Synthesis of K11‐diUb 13: D) Overall synthetic route; E) analytical HPLC chromatogram of purified 13; F) observed ESI‐MS spectrum of purified 13 (23+, 744.9; 21+, 815.7; 19+, 901.5; 17+, 1007.4; 15+, 1141.6; 13+, 1317.1; and 11+, 1556.4); inset: deconvoluted ESI‐MS spectrum of 13 (observed mass = 17 109.3 Da, calculated mass = 17 110.7 Da, average isotopes). Reactions and conditions: activation: 6 m Gn‐HCl, 10 equiv. NaNO2, pH 3.0; ligation: 6 m Gn‐HCl, 40 equiv. MPAA, pH: 6.4; desulfurization: 6 m Gn‐HCl, 500 × 10−3 m TCEP, tBuSH, VA‐044, pH: 6.9; de‐Tfa: 2 m NaOH, pH: 10.0; de‐Thz: methoxyamine‐HCl, pH = 4.0. HPLC (λ = 214 nm).
