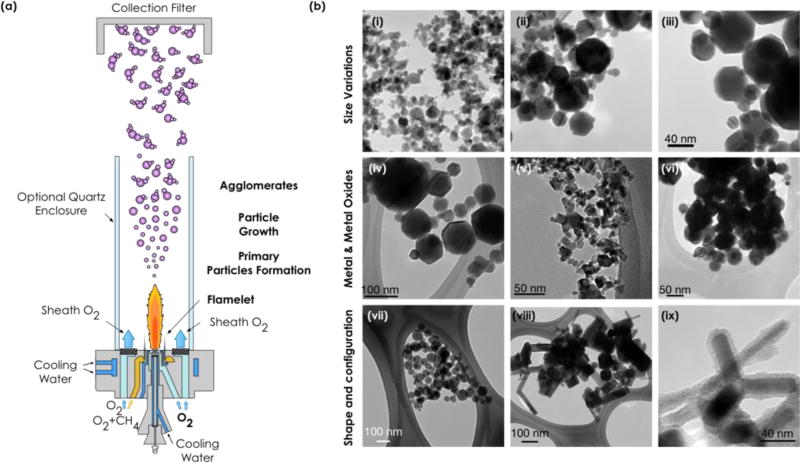
Fig. 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of the Harvard versatile engineered nanomaterials generation system (VENGES) used to synthesize ENMs. (b) TEM images showing the capability and versatility of VENGES to produce a myriad of ENMs, not only the family of reference metals and metal oxides presented in this study but also to produce silica-coated ENMs (i.e. SiO2 coated ZnO) with different size, morphology and configuration. (i-iii) Control in size of iron oxide particles (8nm-i, 25nm-ii and 100nm-iii, images taken under same magnification); (iv-vi) control in type of material (iron oxide-iv, cerium oxide-v and silver-vi); and (vii-ix) control in shape and configuration (spherical-vii, rod shaped-viii and silica coated-ix zinc oxide ENMs). Scale bar in Fig. b-iii is the same for Figs b-i and b-ii.