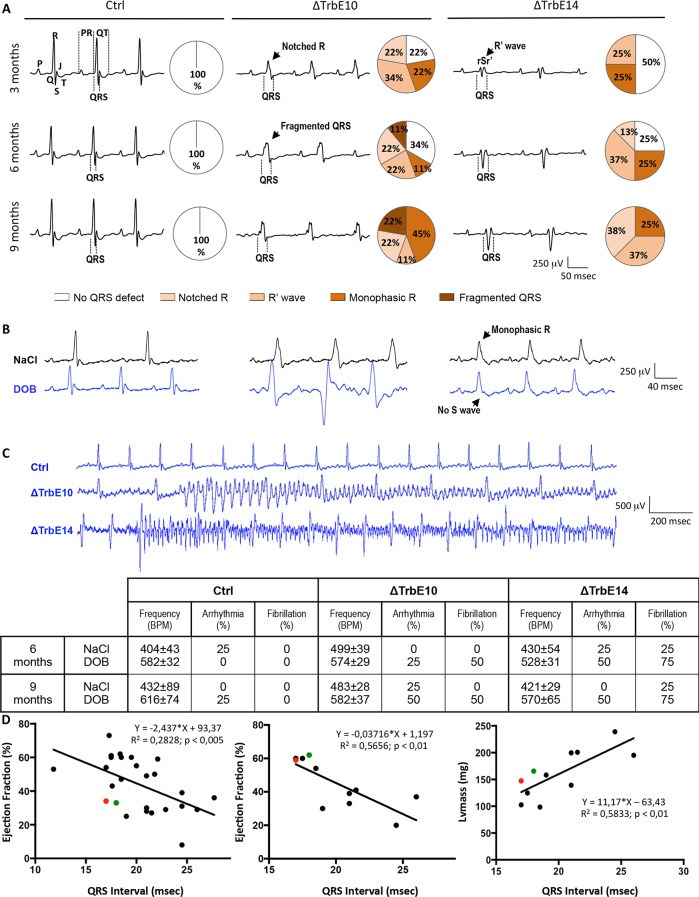
Fig 7. Hypertrabeculated Nkx2-5 mutant hearts exhibit QRS defects, BB blocks and high susceptibility to fibrillation.
(A) Representative tracings from surface ECG measured in lead II in anaesthetized mice at 3-, 6- and 9-month old. In control mice, QRS complexes are normal regardless of the age at which they were recorded. Tracings from Nkx2-5ΔTrbE10 and Nkx2-5ΔTrbE14 mice demonstrated bundle branch block-like appearance with widened QRS complex and a characteristic pattern with Notched R, R' wave and fragmented QRS. (B) Dobutamine caused a marked increase of heart rate in control mice and only a small effect in Nkx2-5ΔTrbE10 and Nkx2-5ΔTrbE14 mice. (C) Severe susceptibility to ventricular fibrillation was found in Nkx2-5ΔTrbE10 and Nkx2-5ΔTrbE14 mutants but not in control mice. Cardiac frequency and quantification of arrhythmias and fibrillation before and after Dobutamine injection are summarized in the table. (D) Plots of QRS duration in lead II from 9-month old mice against Ejection Fraction (EF) recorded during echocardiography (N = 27) and MRI (N = 11) or against LV mass from MRI (N = 11). Red and green dots represent mice with fluctuating EF overtime. Linear relationships were observed and R2 and p-values were indicated for each graph.