Figure 3. Associations of apoE haplotypes with log LDL-TG (left) and RLP-C (right).
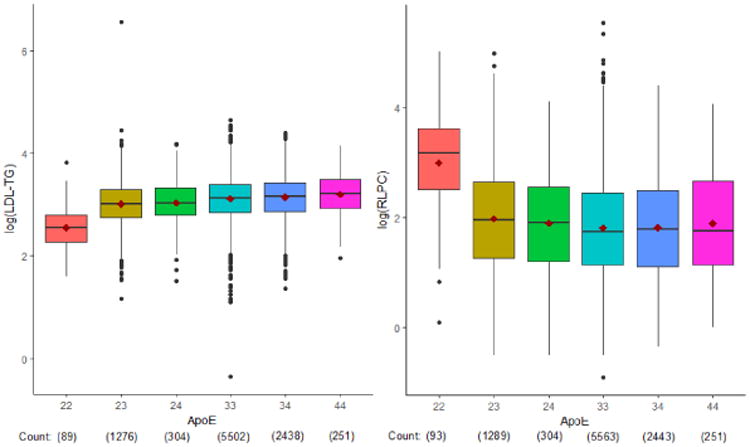
Associations between LDL-TG and RLP-C levels and genetic variants were assessed by whole exome sequencing. A common APOE variant, rs7412, had the strongest association with LDL-TG and RLP-C (p<5×10−8). Since rs7412 defines APOE e2 allele status, we assessed APOE haplotypes and found that APOE e2/2 was associated with reduced LDL-TG and increased RLP-C (p<0.0001 vs any other haplotype). The different relationships of RLP-C and LDL-TG with APOE ε2/2 may be partly explained by the low affinity of apoE2 for the LDL (apoB/E) receptor, potentially leading to delayed clearance of remnant particles. This delayed clearance may lead to increased RLP-C levels, while simultaneously lowering LDL and LDL-TG levels via upregulation of cellular LDL receptors in these individuals.
