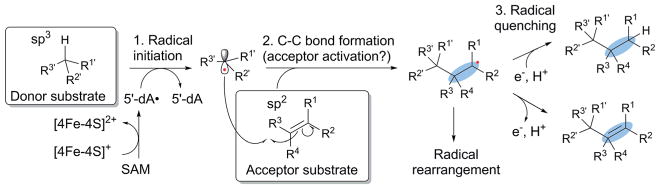
Fig. 2.
Generalized mechanism of C–C bond formation by radical SAM enzymes. Catalysis proceeds through three major steps; (1) radical initiation, (2) C–C bond formation, and (3) radical quenching. C–C bond formation may require activation of the acceptor substrate to achieve efficient and specific reactions. In some enzymes, radical quenching does not take place immediately after the C–C bond formation and the radical intermediate is used for complex radical rearrangement reactions. The C–C bonds formed are highlighted in blue ovals.