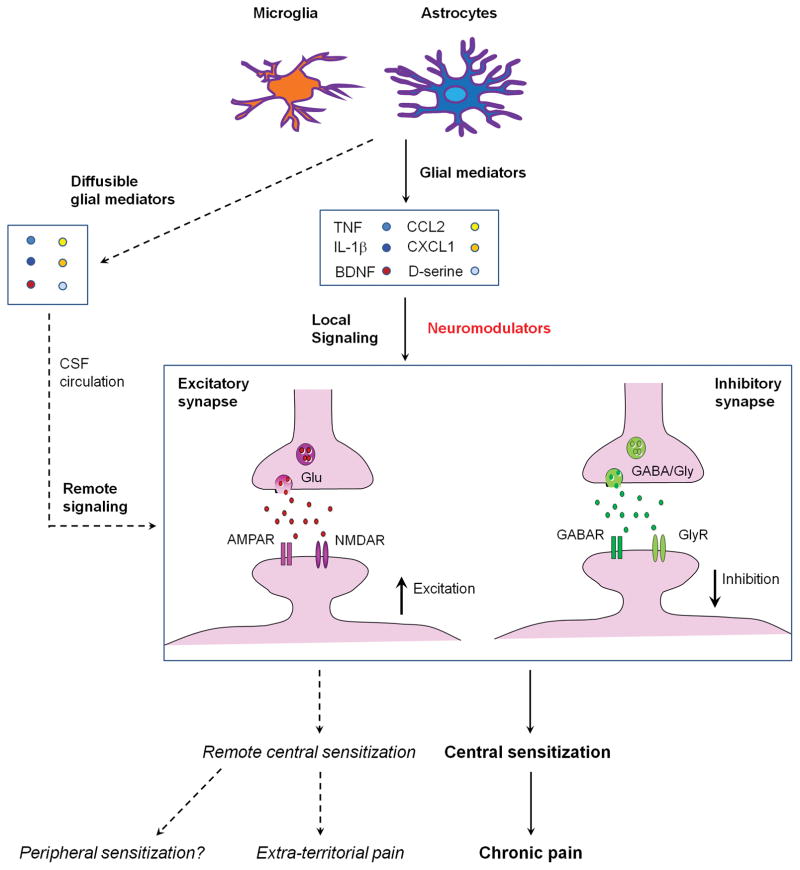
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of local and remote central sensitization induced by glial activation and neuroinflammation in the spinal cord. Activation of spinal microglia and astrocytes by painful insults results in secretion of glial mediators such as TNF, IL-1β, CCL2, CXCL1, BDNF, D-serine, which can act as neuromodulators to induce local central sensitization in surrounding excitatory synapses (facilitation) and inhibitory synapses (dis-inhibition). During neuroinflammation these glial mediators are also present in the CSF and affect synapses in different spinal segments to cause remote central sensitization and extra-territorial and widespread pain beyond the initial injury site.