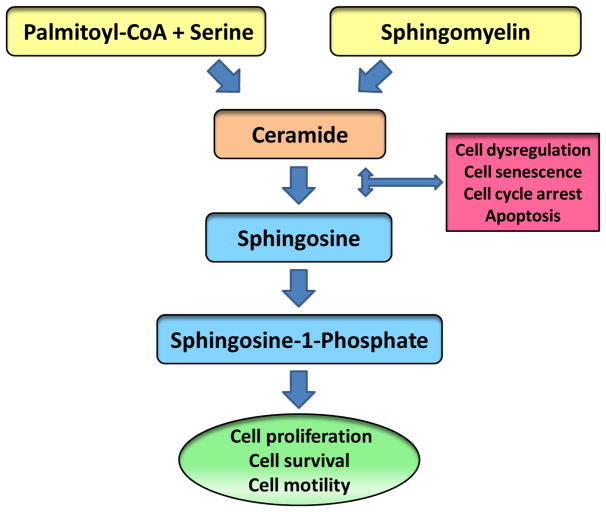
Figure 1. Regulatory roles of CER signaling steps in cell survival and apoptosis.
CER can be generated intracellularly via the de novo and recycling pathways. In the de novo pathway, palmitoyl-CoA and serine are converted to CER, a step catalyzed by serine palmitoyl transferase. In the recycling pathway, CER is formed via degradation of sphingomyelins; these steps are mediated by a variety of sphingomyelinases. CER is converted sphingosine by ceramidase. Sphingosine is converted to sphingosine-1-phosphate by sphingosine kinase. It is noteworthy that both CER and sphingosine have been shown to promote cell cycle arrest and cell senescence and induce cell apoptosis. Interestingly, however, sphingosine-1-phosphate exerts positive modulatory effects on cell function including cell proliferation, motility and survival. Therefore, intermediates of these pathway play both positive and negative modulatory roles in cell function.