Figure 3. A proposed model for Rac1-CER signaling cascade in the genesis of islet dysfunction under conditions of metabolic stress and exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines.
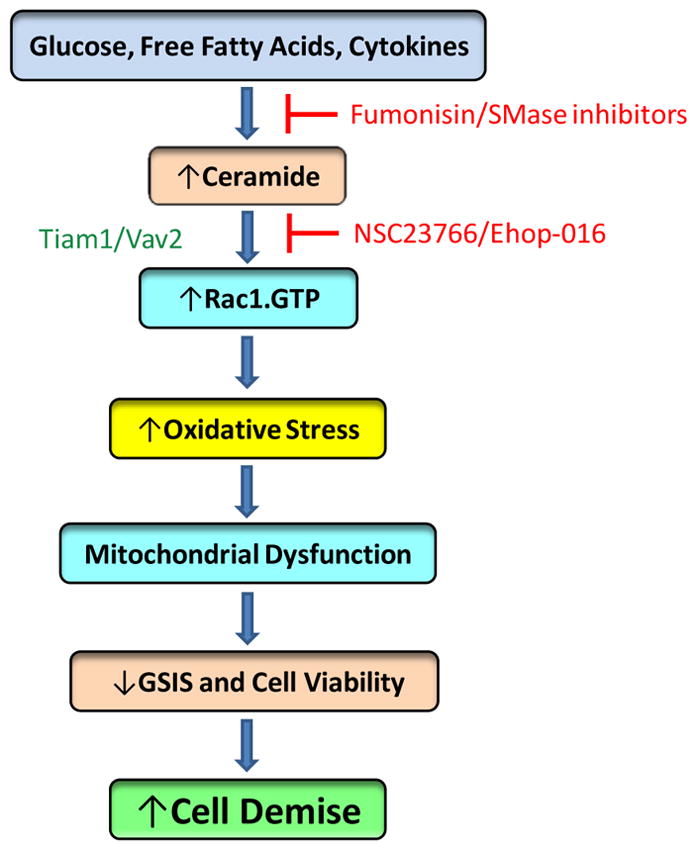
Exposure of islet β-cells to high glucose, saturated fatty acids and cytokines leads to generation of intracellular CER, which, in turn, promotes Rac1 activation by its GEFS, namely Tiam1/Vav2. It should be noted that, at least, in the context of islet β-cell, roles of Vav2 in CER-induced activation of Rac1 have not been demonstrated. Constitutively activated Rac1 promotes activation of Nox2 resulting in increased oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysregulation, impaired GSIS, loss in metabolic cell viability resulting in cell apoptosis (see text for additional details) .
