Figure 2. Post-Injury Ketamine Inhibits Neurogenesis after CCI.
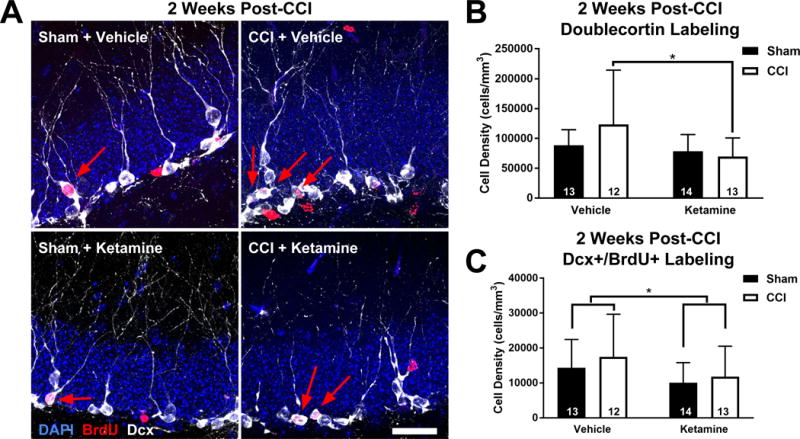
(A) Representative images of the dentate granule cell layer from each treatment group 2 weeks post-injury. Immature neurons are stained with for doublecortin (Dcx; white), along with BrdU-labeled cells (red) and DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate BrdU+/Dcx+ co-labeled cells. Scale bar = 25 μm. (B) Analysis of Dcx labeling at 2 WPI demonstrates that ketamine suppressed neurogenesis after CCI. (C) Ketamine administration suppressed the number of neurons born 2-3 days after injury, as identified using the density of BrdU+/Dcx+ co-labeled cells. Bars represent mean cell densities (cells/mm3) and error bars represent SD; numbers inside bars represent the N for each group; * p < 0.05.
