Figure 6. AURKA transcription is regulated by MYC downstream of the PI3K-pathway.
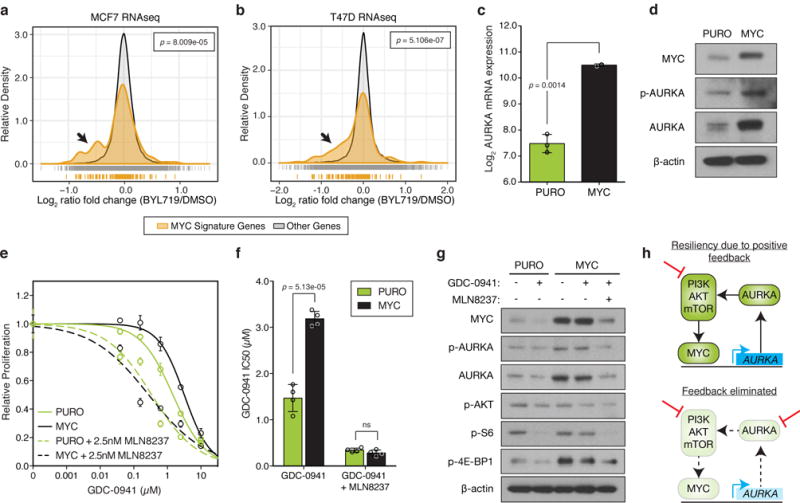
(a,b) Histogram of normalized gene expression of all 150 genes in the MYC gene signature compared to genes not in this signature for (a) MCF7 or (b) T47D cells treated with 1μM BYL719 or DMSO for 24 hours. BYL719 treatment data obtained from Bosch, et al.17 and p values determined by Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. (c) Relative levels of AURKA mRNA in an isogenic pair of control (PURO, n=3 independent samples) or MYC expressing MCF10A cells (n=2 independent samples) measured by RT-PCR. (d) Immunoblot of protein lysates from PURO or MYC cells representative of n=3 independent experiments with similar results (full blots shown in Supplementary Fig. 18a). (e) Proliferation of control or MYC cells in response to GDC-0941 or treated with the combination of 2.5nM MLN8237. Combinations were normalized to MLN8237 alone. Data represents n=4 biologically independent samples. (f) IC50 analysis of dose-response curves shown in (e) from n=4 independent samples. (g) Immunoblot of lysates from control and MYC MCF10A cells treated with 1μM of GDC-0941 or 100nM of MLN8237 for 24 hours. Representative image of n=3 independent experiments with similar results (full blots shown in Supplementary Fig. 18b). (h) Proposed model of positive feedback loop between the PI3K-pathway, MYC and AURKA. In all graphs, error bars are mean ± s.d. and p values calculated using a two-sided t-test, unless otherwise indicated.
